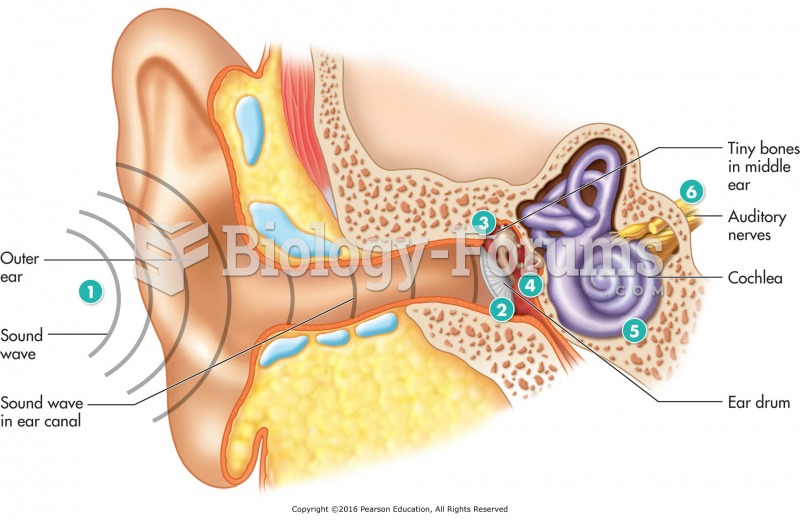
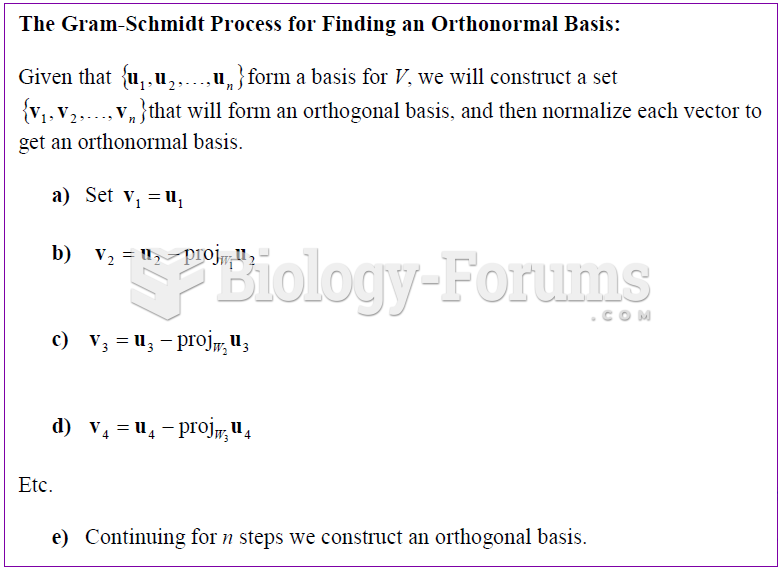
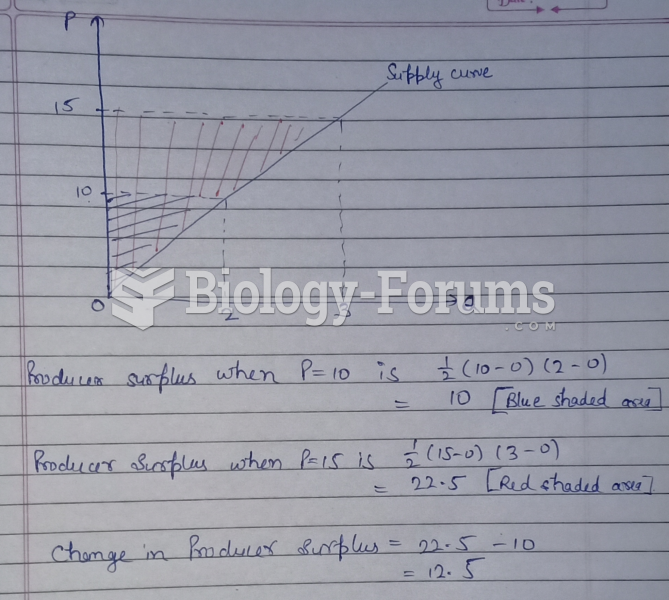
Answer to Question 1
Answer: 1; 2; 3; 4
Rationale:
Let me talk to the vendor and see if they can come and talk to us about the best way to use this lotion with the product. The nurse manager must assist the staff members during the change process. It is appropriate for the nurse manager to act as a liaison between the staff members and the vendor and educators about the process change.
Remember, we decided to use this product because our clients were reporting that their skin was drying out with our old way of bathing them. The nurse manager must assist the staff members during the change process. It is important for the nurse manager to remind staff members about the reason for the change. This helps the staff members psychologically adjust to the change.
I'm sorry, but you cannot use the old product on the client. The nurse manager must assist the staff members during the change process. It is not appropriate to allow some staff members to return to the old way of doing something. The change is not optional.
Let's all meet in the conference room after this shift to see how the change is going. The nurse manager must assist the staff members during the change process. It is important for the nurse manager to determine how well the staff is responding to the change and what problems are occurring regarding the change.
After this change, I'm not making you guys change anything for a long time. The nurse manager must assist the staff members during the change process. It is not appropriate for the nurse manager to state that there will be no new changes after a change has been made. Sometimes, changes are radical interventions, and staff members must strive to uphold their professional values with change. Some change is inevitable.
Answer to Question 2
Answer: 1; 4
Rationale:
The staff members identify feasible solutions to the problem. The change process can be broken down into unfreezing, moving, and refreezing stages. The moving stage involves identifying methods for solving problems. This stage requires re-education of staff members.
The nurse manager shares information with the staff about why a change is needed. The change process can be broken down into unfreezing, moving, and refreezing stages. The nurse manager shares information about why a change is needed during the unfreezing stage.
The nursing manager identifies staff members who might be allies during the change process. The change process can be broken down into unfreezing, moving, and refreezing stages. The nurse manager should identify allies during the unfreezing stage. Identifying allies early in the change process can help reduce organizational costs related to change. This stage requires interactive leadership. The nurse manager must communicate well with staff members, pay attention to group dynamics, and assist with conflict management.
The process change is piloted on the night shift. The change process can be broken down into unfreezing, moving, and refreezing stages. This behavior takes place during the moving stage. It is important to provide staff members with the opportunity to practice new behaviors in small-scale pilots prior to implementation of the change.
The new behaviors have been internalized by staff members on all shifts. The change process can be broken down into unfreezing, moving, and refreezing stages. This occurs during the refreezing stage. During this stage, the new practice is stabilized, integrated, and internalized by staff members.