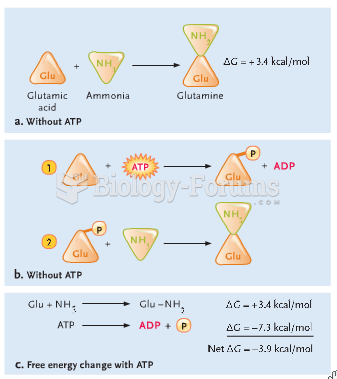
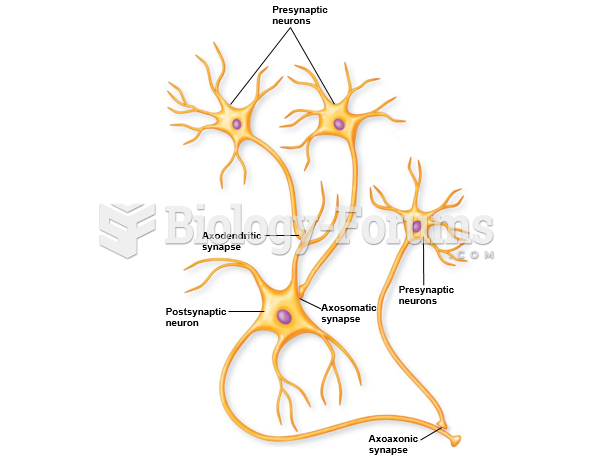
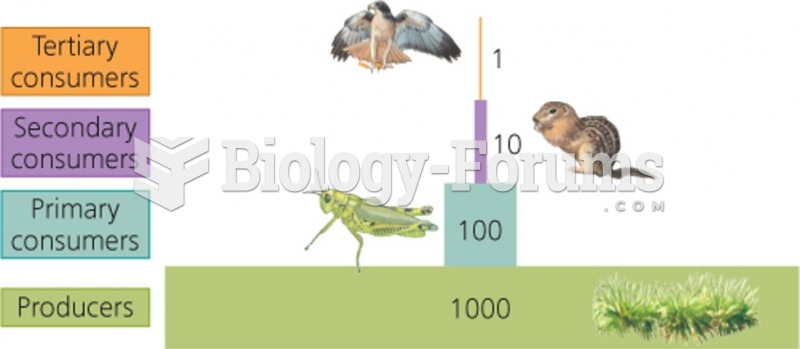
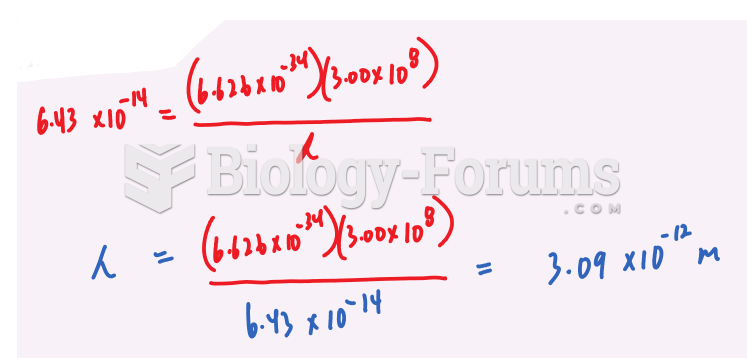
|
|
|
Anti-aging claims should not ever be believed. There is no supplement, medication, or any other substance that has been proven to slow or stop the aging process.
ACTH levels are normally highest in the early morning (between 6 and 8 A.M.) and lowest in the evening (between 6 and 11 P.M.). Therefore, a doctor who suspects abnormal levels looks for low ACTH in the morning and high ACTH in the evening.
Elderly adults are living longer, and causes of death are shifting. At the same time, autopsy rates are at or near their lowest in history.
In 1835 it was discovered that a disease of silkworms known as muscardine could be transferred from one silkworm to another, and was caused by a fungus.
As many as 20% of Americans have been infected by the fungus known as Histoplasmosis. While most people are asymptomatic or only have slight symptoms, infection can progress to a rapid and potentially fatal superinfection.