|
|
|
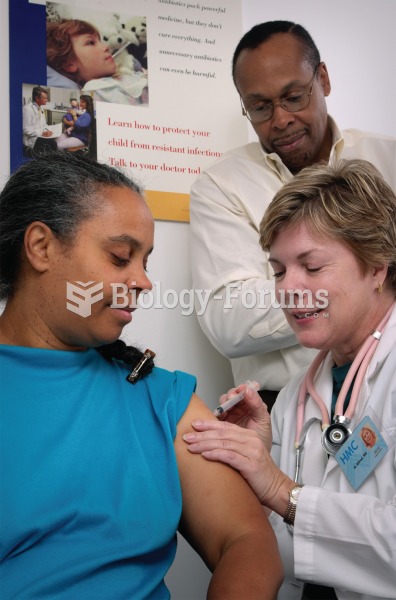
In inpatient settings, adverse drug events account for an estimated one in three of all hospital adverse events. They affect approximately 2 million hospital stays every year, and prolong hospital stays by between one and five days.
There used to be a metric calendar, as well as metric clocks. The metric calendar, or "French Republican Calendar" divided the year into 12 months, but each month was divided into three 10-day weeks. Each day had 10 decimal hours. Each hour had 100 decimal minutes. Due to lack of popularity, the metric clocks and calendars were ended in 1795, three years after they had been first marketed.
Medications that are definitely not safe to take when breastfeeding include radioactive drugs, antimetabolites, some cancer (chemotherapy) agents, bromocriptine, ergotamine, methotrexate, and cyclosporine.
Multiple experimental evidences have confirmed that at the molecular level, cancer is caused by lesions in cellular DNA.
Though newer “smart” infusion pumps are increasingly becoming more sophisticated, they cannot prevent all programming and administration errors. Health care professionals that use smart infusion pumps must still practice the rights of medication administration and have other professionals double-check all high-risk infusions.