|
|
|
Alcohol acts as a diuretic. Eight ounces of water is needed to metabolize just 1 ounce of alcohol.
Bisphosphonates were first developed in the nineteenth century. They were first investigated for use in disorders of bone metabolism in the 1960s. They are now used clinically for the treatment of osteoporosis, Paget's disease, bone metastasis, multiple myeloma, and other conditions that feature bone fragility.
You should not take more than 1,000 mg of vitamin E per day. Doses above this amount increase the risk of bleeding problems that can lead to a stroke.
GI conditions that will keep you out of the U.S. armed services include ulcers, varices, fistulas, esophagitis, gastritis, congenital abnormalities, inflammatory bowel disease, enteritis, colitis, proctitis, duodenal diverticula, malabsorption syndromes, hepatitis, cirrhosis, cysts, abscesses, pancreatitis, polyps, certain hemorrhoids, splenomegaly, hernias, recent abdominal surgery, GI bypass or stomach stapling, and artificial GI openings.
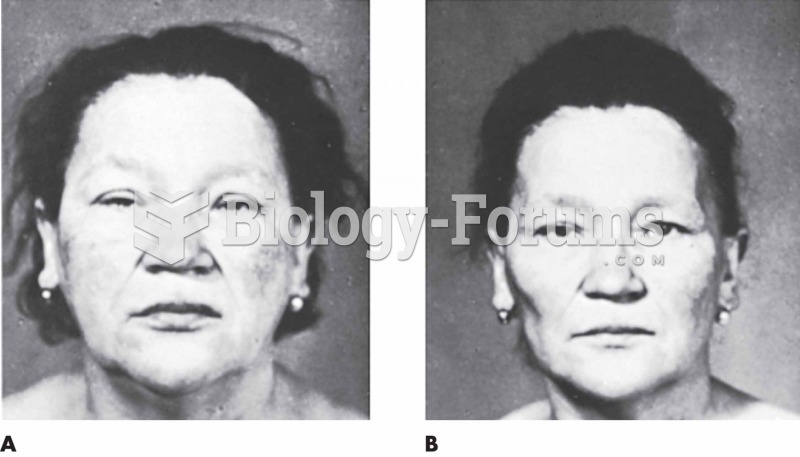
The toxic levels for lithium carbonate are close to the therapeutic levels. Signs of toxicity include fine hand tremor, polyuria, mild thirst, nausea, general discomfort, diarrhea, vomiting, drowsiness, muscular weakness, lack of coordination, ataxia, giddiness, tinnitus, and blurred vision.