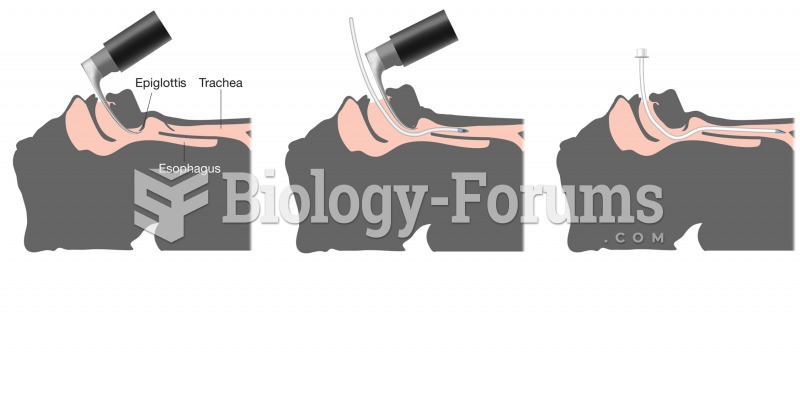
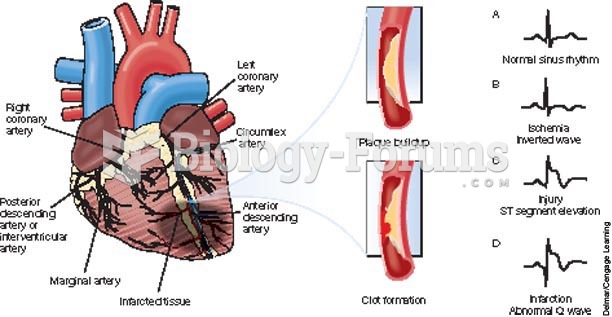
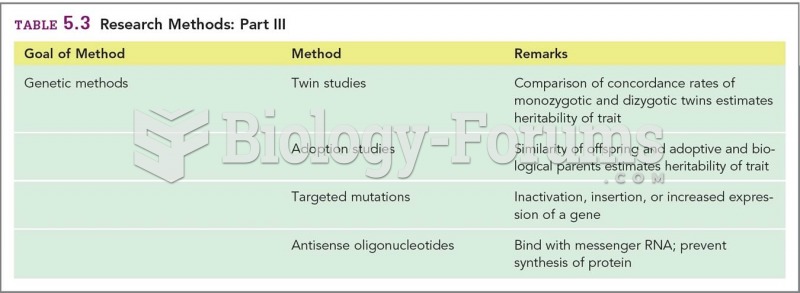
|
|
|
Adolescents often feel clumsy during puberty because during this time of development, their hands and feet grow faster than their arms and legs do. The body is therefore out of proportion. One out of five adolescents actually experiences growing pains during this period.
When Gabriel Fahrenheit invented the first mercury thermometer, he called "zero degrees" the lowest temperature he was able to attain with a mixture of ice and salt. For the upper point of his scale, he used 96°, which he measured as normal human body temperature (we know it to be 98.6° today because of more accurate thermometers).
Women are 50% to 75% more likely than men to experience an adverse drug reaction.
Illicit drug use costs the United States approximately $181 billion every year.
In 1886, William Bates reported on the discovery of a substance produced by the adrenal gland that turned out to be epinephrine (adrenaline). In 1904, this drug was first artificially synthesized by Friedrich Stolz.