|
|
|
Automated pill dispensing systems have alarms to alert patients when the correct dosing time has arrived. Most systems work with many varieties of medications, so patients who are taking a variety of drugs can still be in control of their dose regimen.
On average, someone in the United States has a stroke about every 40 seconds. This is about 795,000 people per year.
Alzheimer's disease affects only about 10% of people older than 65 years of age. Most forms of decreased mental function and dementia are caused by disuse (letting the mind get lazy).
Less than one of every three adults with high LDL cholesterol has the condition under control. Only 48.1% with the condition are being treated for it.
Thyroid conditions cause a higher risk of fibromyalgia and chronic fatigue syndrome.
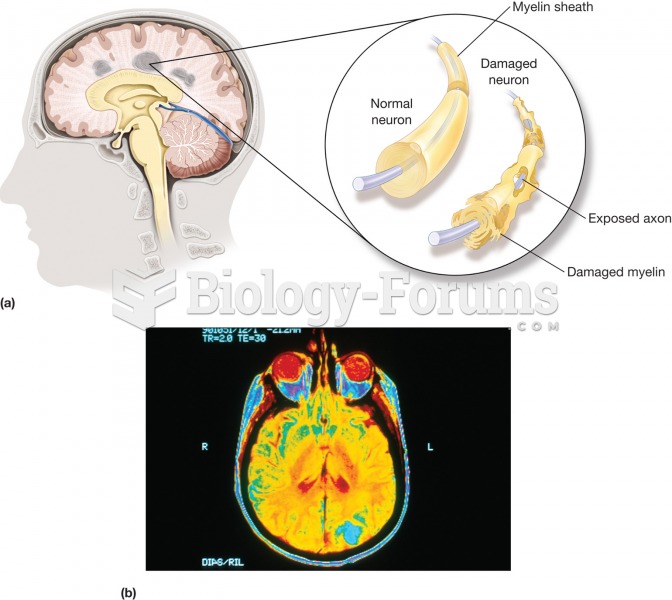 Multiple sclerosis (MS). (a) A disease characterized by the gradual development of small areas of ha
Multiple sclerosis (MS). (a) A disease characterized by the gradual development of small areas of ha
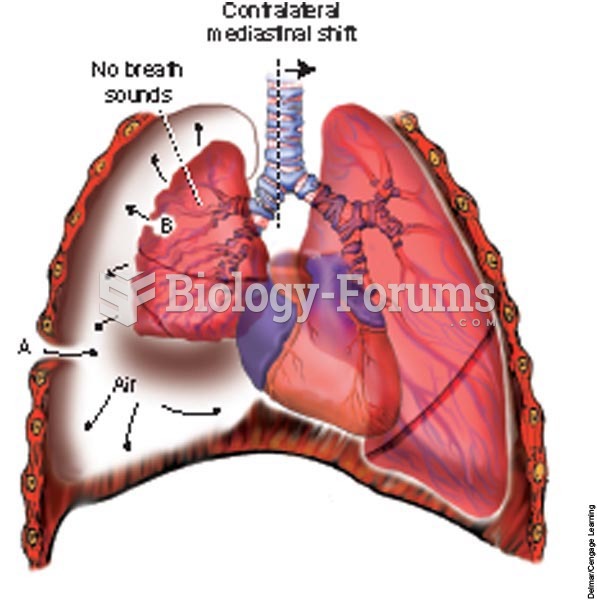
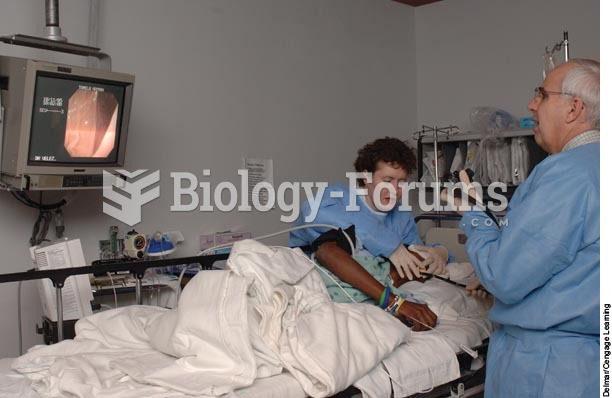 A client is having an endoscopy performed by a physician who views the upper gastrointestinal intern
A client is having an endoscopy performed by a physician who views the upper gastrointestinal intern
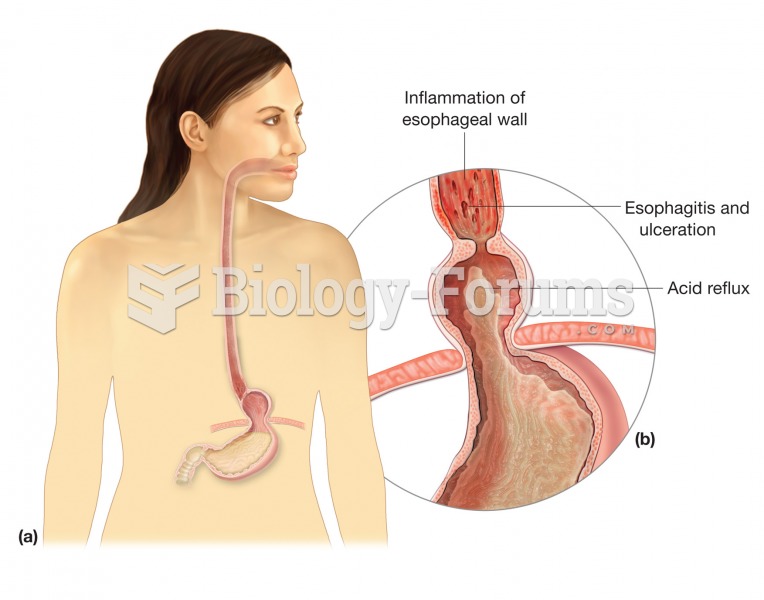
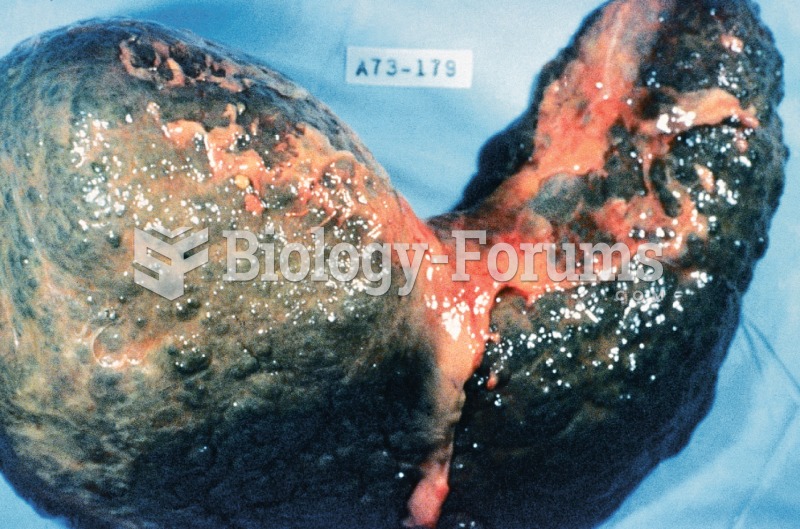 Cirrhosis. Cirrhosis is characterized by a chronic deterioration of the liver, replacing healthy cel
Cirrhosis. Cirrhosis is characterized by a chronic deterioration of the liver, replacing healthy cel