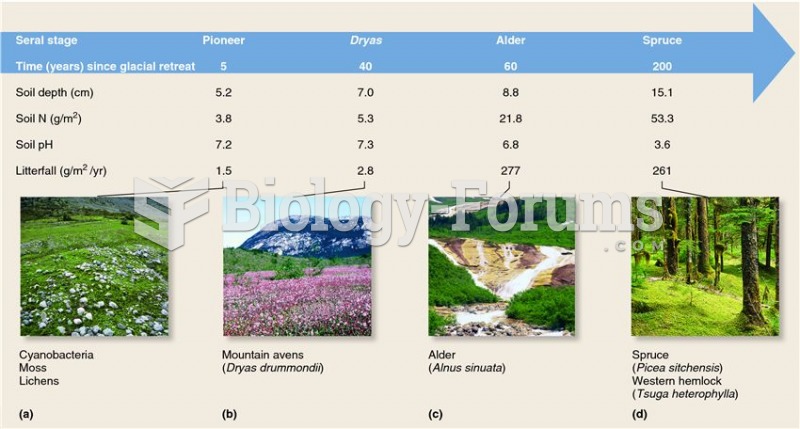
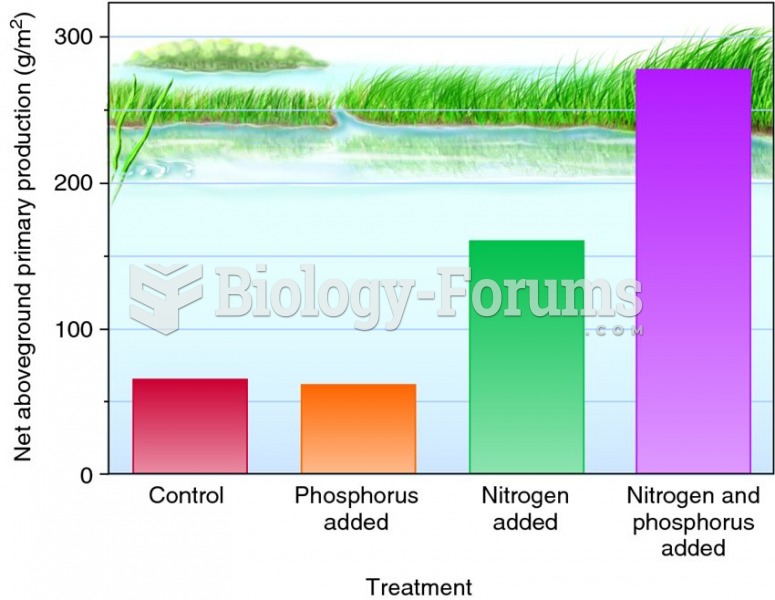
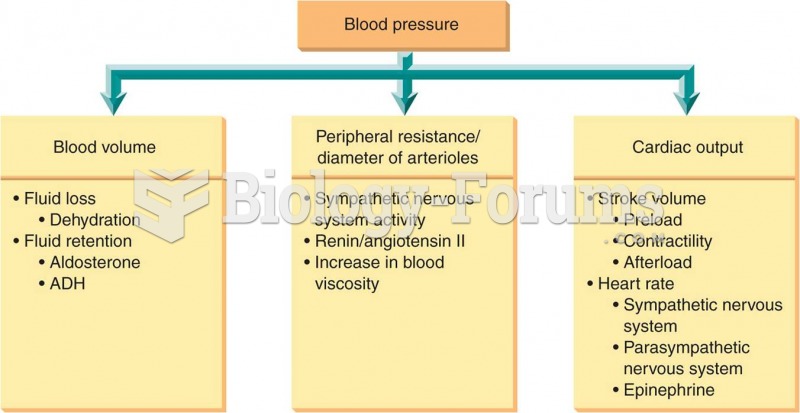
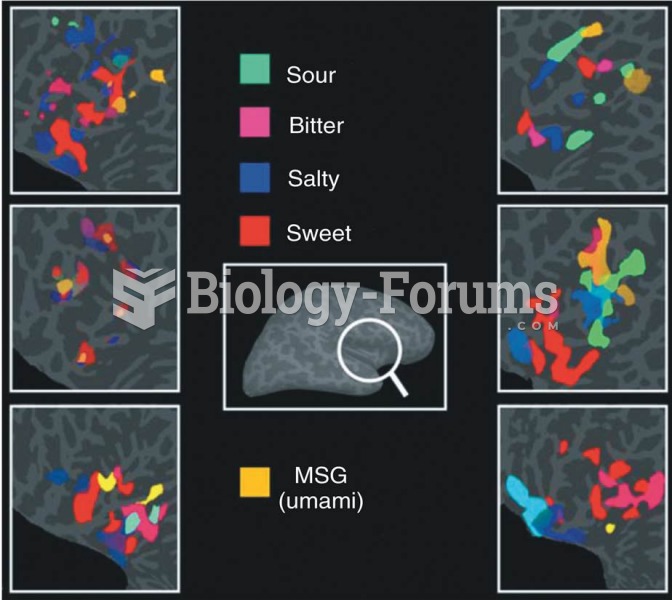
|
|
|
Fatal fungal infections may be able to resist newer antifungal drugs. Globally, fungal infections are often fatal due to the lack of access to multiple antifungals, which may be required to be utilized in combination. Single antifungals may not be enough to stop a fungal infection from causing the death of a patient.
After a vasectomy, it takes about 12 ejaculations to clear out sperm that were already beyond the blocked area.
The longest a person has survived after a heart transplant is 24 years.
The average adult has about 21 square feet of skin.
The use of salicylates dates back 2,500 years to Hippocrates’s recommendation of willow bark (from which a salicylate is derived) as an aid to the pains of childbirth. However, overdosage of salicylates can harm body fluids, electrolytes, the CNS, the GI tract, the ears, the lungs, the blood, the liver, and the kidneys and cause coma or death.