|
|
|
Fungal nail infections account for up to 30% of all skin infections. They affect 5% of the general population—mostly people over the age of 70.
GI conditions that will keep you out of the U.S. armed services include ulcers, varices, fistulas, esophagitis, gastritis, congenital abnormalities, inflammatory bowel disease, enteritis, colitis, proctitis, duodenal diverticula, malabsorption syndromes, hepatitis, cirrhosis, cysts, abscesses, pancreatitis, polyps, certain hemorrhoids, splenomegaly, hernias, recent abdominal surgery, GI bypass or stomach stapling, and artificial GI openings.
The heart is located in the center of the chest, with part of it tipped slightly so that it taps against the left side of the chest.
Vampire bats have a natural anticoagulant in their saliva that permits continuous bleeding after they painlessly open a wound with their incisors. This capillary blood does not cause any significant blood loss to their victims.
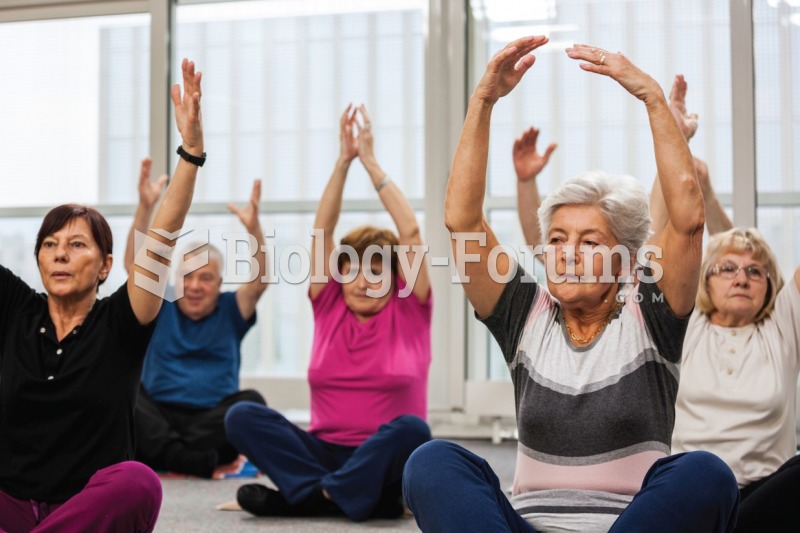
Elderly adults are at greatest risk of stroke and myocardial infarction and have the most to gain from prophylaxis. Patients ages 60 to 80 years with blood pressures above 160/90 mm Hg should benefit from antihypertensive treatment.
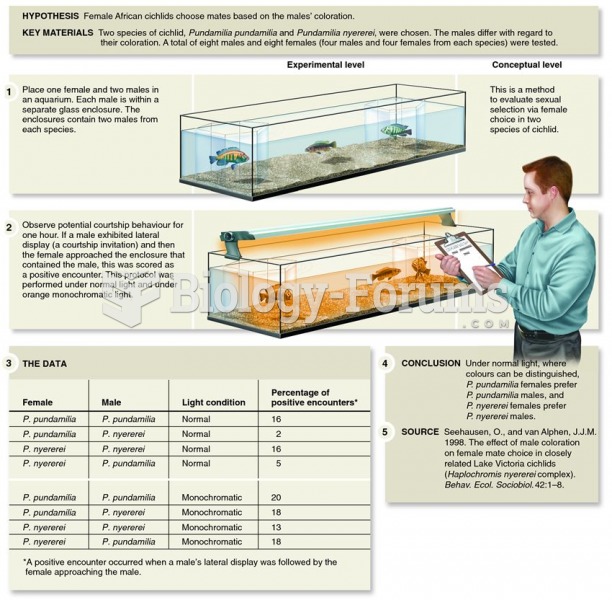 A study by Seehausen and van Alphen involving the effects of male coloration on female choice in Afr
A study by Seehausen and van Alphen involving the effects of male coloration on female choice in Afr
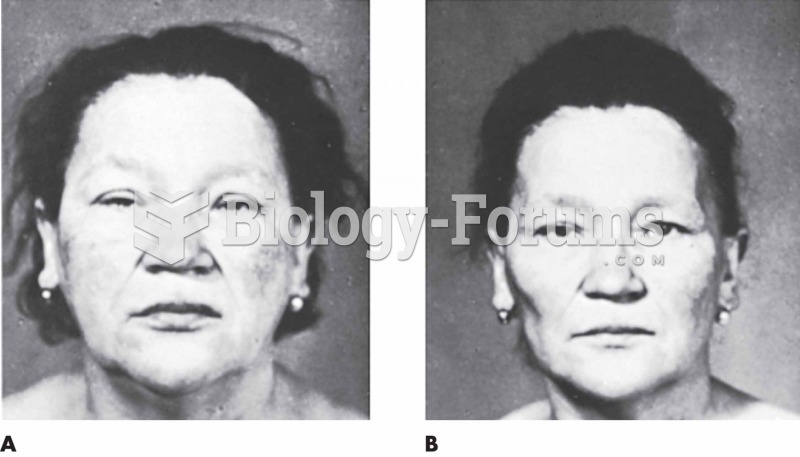 (A) A 62-year-old patient with myxedema exhibiting marked edema of the face and a somnolent look. Th
(A) A 62-year-old patient with myxedema exhibiting marked edema of the face and a somnolent look. Th