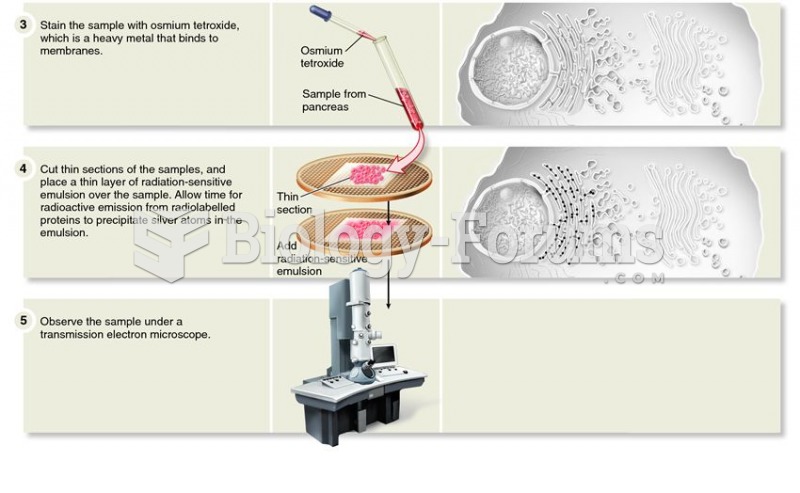
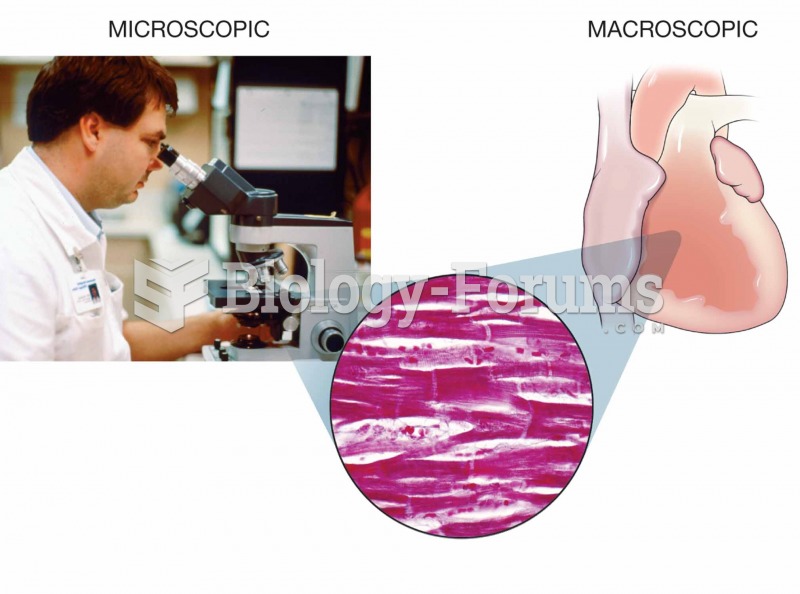
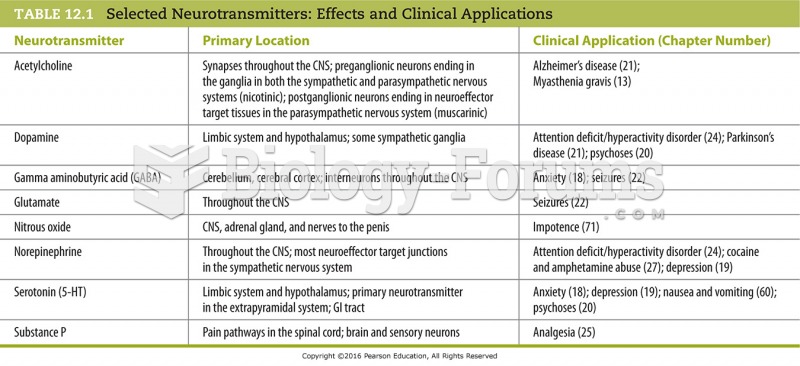
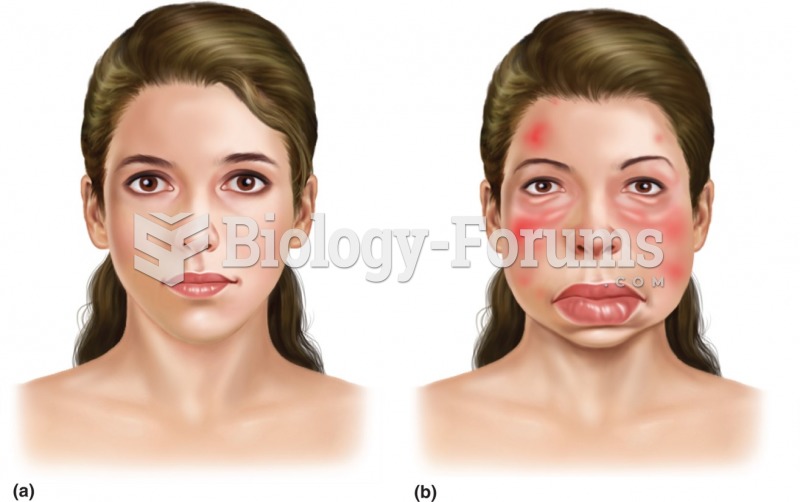
|
|
|
Pregnant women usually experience a heightened sense of smell beginning late in the first trimester. Some experts call this the body's way of protecting a pregnant woman from foods that are unsafe for the fetus.
Aspirin is the most widely used drug in the world. It has even been recognized as such by the Guinness Book of World Records.
Blastomycosis is often misdiagnosed, resulting in tragic outcomes. It is caused by a fungus living in moist soil, in wooded areas of the United States and Canada. If inhaled, the fungus can cause mild breathing problems that may worsen and cause serious illness and even death.
About one in five American adults and teenagers have had a genital herpes infection—and most of them don't know it. People with genital herpes have at least twice the risk of becoming infected with HIV if exposed to it than those people who do not have genital herpes.
There can actually be a 25-hour time difference between certain locations in the world. The International Date Line passes between the islands of Samoa and American Samoa. It is not a straight line, but "zig-zags" around various island chains. Therefore, Samoa and nearby islands have one date, while American Samoa and nearby islands are one day behind. Daylight saving time is used in some islands, but not in others—further shifting the hours out of sync with natural time.