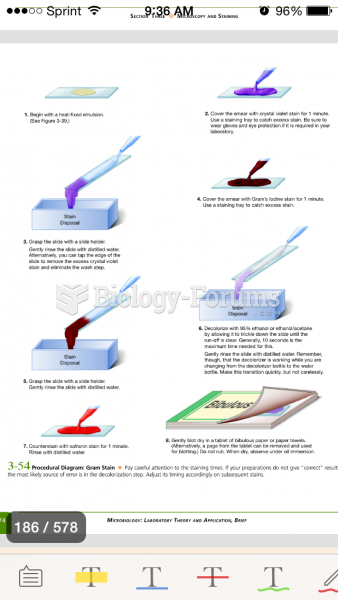
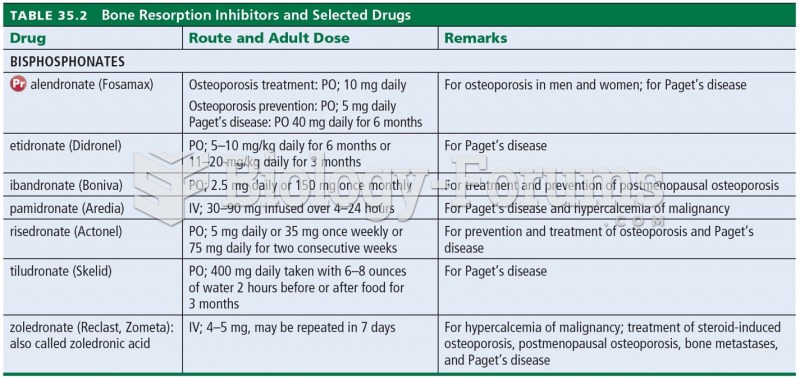
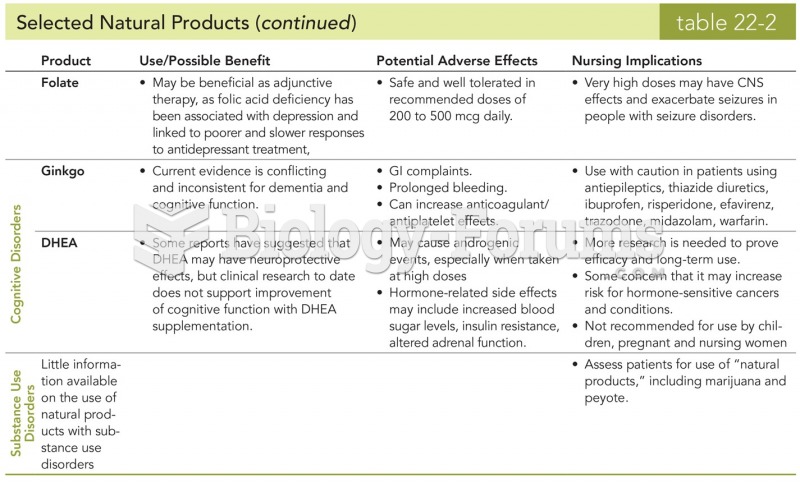
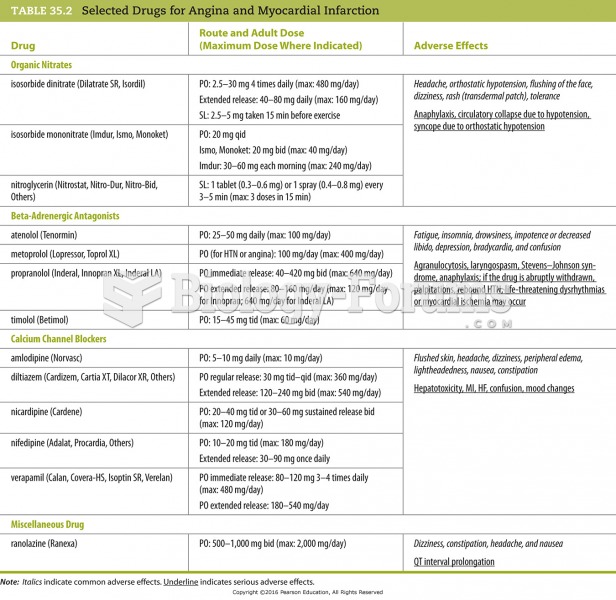
matching
a. A probability sampling procedure wherein units of subjects are selected, rather than the subjects themselves.
b. An unbiased criterion used in the selection of subjects for a sample.
c. The type of sampling used when the likelihood of selecting any one member of the population is known.
d. A stratified random sampling procedure wherein subjects in the sample are selected in proportion to how they are represented in the population.
e. The magnitude of the difference between the characteristics of the sample and the characteristics of the population from which it was selected.
f. The ability to draw inferences and conclusions from data.
g. A sampling procedure allowing for the equal and independent chance of subjects being selected as part of the sample.
h. A representative portion of a population.
i. The process of selecting a sample that represents different groups or levels of a population.
j. A random sampling procedure in which increments determine who becomes part of the sample; for example, every third person is selected.
k. A nonprobability sampling procedure wherein the selected sample represents a captive audience; for example, sophomore college students in an introductory psychology class.
l. A random sampling procedure used when subjects are known to be unequal on some variable in the population.
m. A nonprobability sampling procedure similar to stratified random sampling in that a particular stratum is the focus; however, a specified number is set to be selected and once that number is met, no further selection occurs.
n. When the likelihood of selecting any one member of the population is unknown.
1. Sample
2. Generalizability
3. Probability Sampling
4. Nonprobability Sampling
5. Simple Random Sampling
6. Table of Random Numbers
7. Systematic Sampling
8. Stratified Sampling
9. Stratified Random Sampling
10. Cluster Sampling
11. Convenience Sampling
12. Quota Sampling
13. Proportional Stratified Sampling
14. Sampling Error
Question 2
From looking at a research matrix, one can infer the researcher's tasks.
Indicate whether the statement is true or false