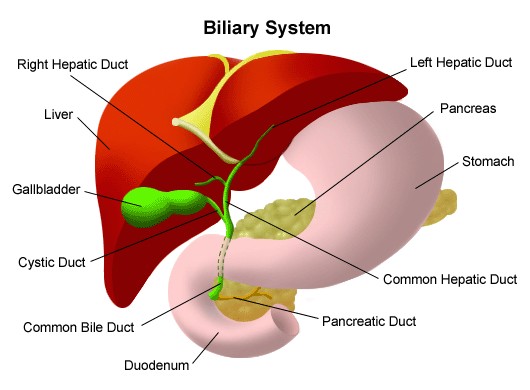
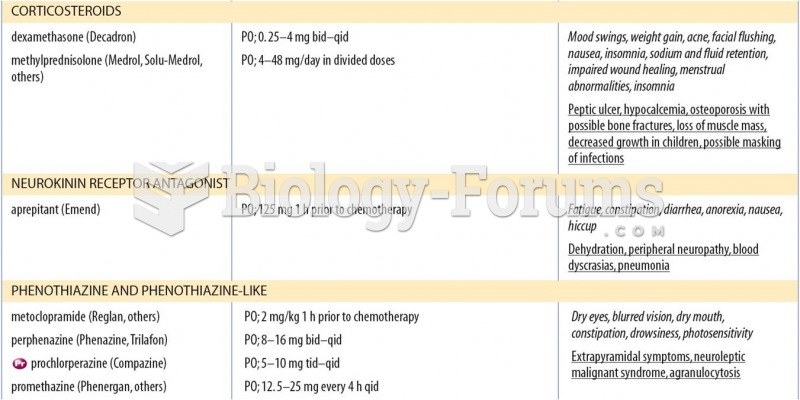
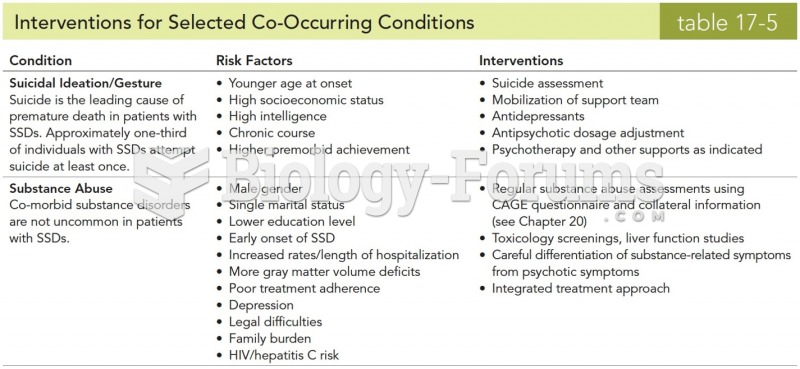
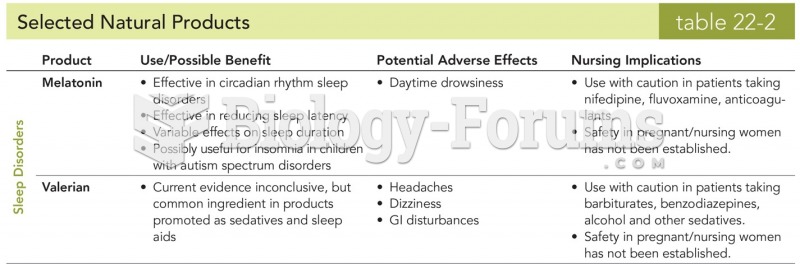
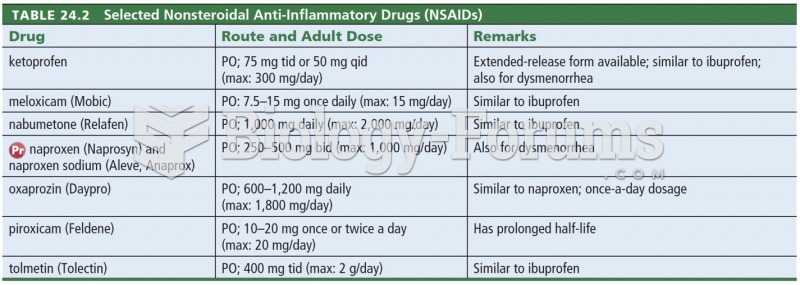
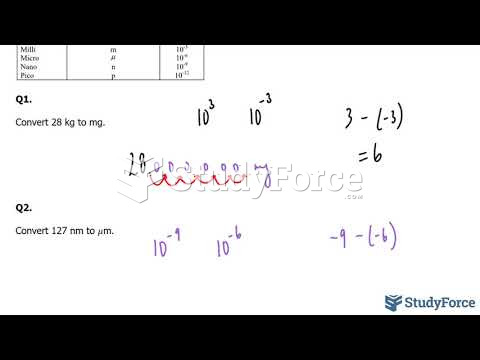
|
|
|
Nearly all drugs pass into human breast milk. How often a drug is taken influences the amount of drug that will pass into the milk. Medications taken 30 to 60 minutes before breastfeeding are likely to be at peak blood levels when the baby is nursing.
When blood is deoxygenated and flowing back to the heart through the veins, it is dark reddish-blue in color. Blood in the arteries that is oxygenated and flowing out to the body is bright red. Whereas arterial blood comes out in spurts, venous blood flows.
Fewer than 10% of babies are born on their exact due dates, 50% are born within 1 week of the due date, and 90% are born within 2 weeks of the date.
Signs of depression include feeling sad most of the time for 2 weeks or longer; loss of interest in things normally enjoyed; lack of energy; sleep and appetite disturbances; weight changes; feelings of hopelessness, helplessness, or worthlessness; an inability to make decisions; and thoughts of death and suicide.
Long-term mental and physical effects from substance abuse include: paranoia, psychosis, immune deficiencies, and organ damage.