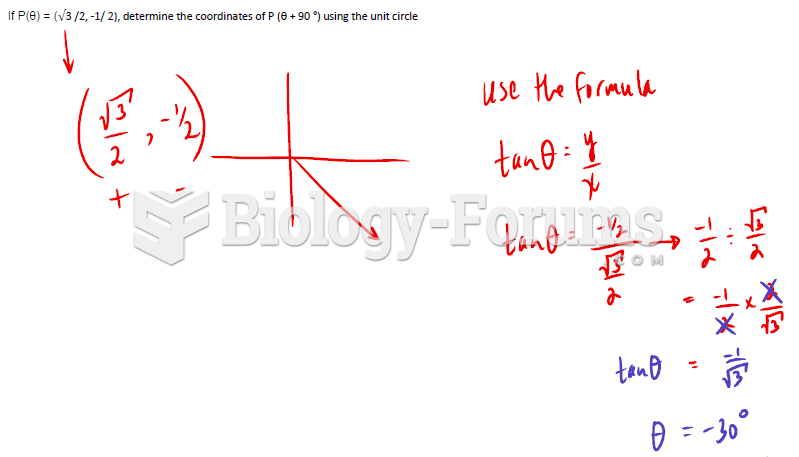
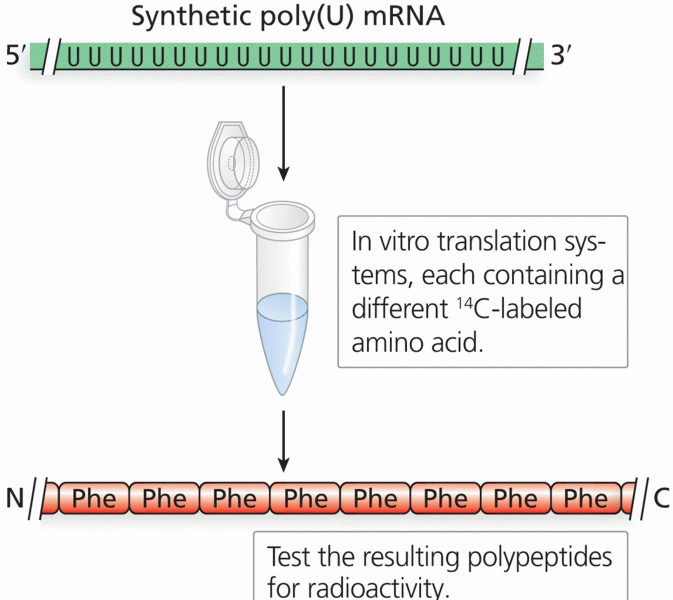
|
|
|
A good example of polar molecules can be understood when trying to make a cake. If water and oil are required, they will not mix together. If you put them into a measuring cup, the oil will rise to the top while the water remains on the bottom.
Adult head lice are gray, about ? inch long, and often have a tiny dot on their backs. A female can lay between 50 and 150 eggs within the several weeks that she is alive. They feed on human blood.
The training of an anesthesiologist typically requires four years of college, 4 years of medical school, 1 year of internship, and 3 years of residency.
As many as 20% of Americans have been infected by the fungus known as Histoplasmosis. While most people are asymptomatic or only have slight symptoms, infection can progress to a rapid and potentially fatal superinfection.
Cutaneous mucormycosis is a rare fungal infection that has been fatal in at least 29% of cases, and in as many as 83% of cases, depending on the patient's health prior to infection. It has occurred often after natural disasters such as tornados, and early treatment is essential.