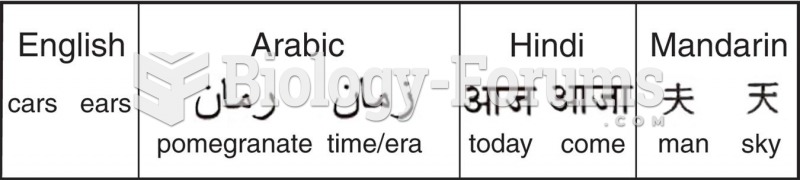
|
|
|
Most childhood vaccines are 90–99% effective in preventing disease. Side effects are rarely serious.
Hypertension is a silent killer because it is deadly and has no significant early symptoms. The danger from hypertension is the extra load on the heart, which can lead to hypertensive heart disease and kidney damage. This occurs without any major symptoms until the high blood pressure becomes extreme. Regular blood pressure checks are an important method of catching hypertension before it can kill you.
Coca-Cola originally used coca leaves and caffeine from the African kola nut. It was advertised as a therapeutic agent and "pickerupper." Eventually, its formulation was changed, and the coca leaves were removed because of the effects of regulation on cocaine-related products.
Cutaneous mucormycosis is a rare fungal infection that has been fatal in at least 29% of cases, and in as many as 83% of cases, depending on the patient's health prior to infection. It has occurred often after natural disasters such as tornados, and early treatment is essential.
Anesthesia awareness is a potentially disturbing adverse effect wherein patients who have been paralyzed with muscle relaxants may awaken. They may be aware of their surroundings but unable to communicate or move. Neurologic monitoring equipment that helps to more closely check the patient's anesthesia stages is now available to avoid the occurrence of anesthesia awareness.
 Differences in how we display gender often lie below our awareness. How males and females use social ...
Differences in how we display gender often lie below our awareness. How males and females use social ...
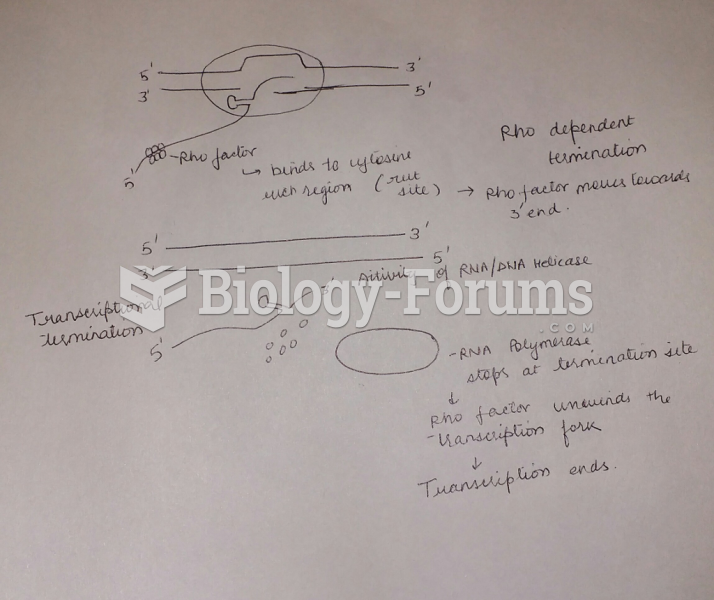 Draw and label a diagram and explain how a factor-dependent transcription (rho-dependent) terminator
Draw and label a diagram and explain how a factor-dependent transcription (rho-dependent) terminator