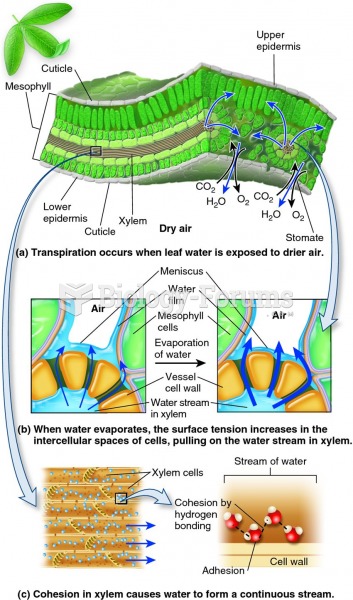
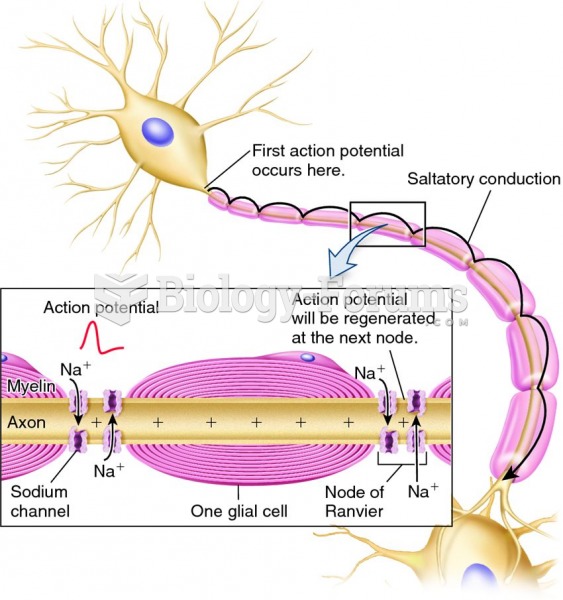
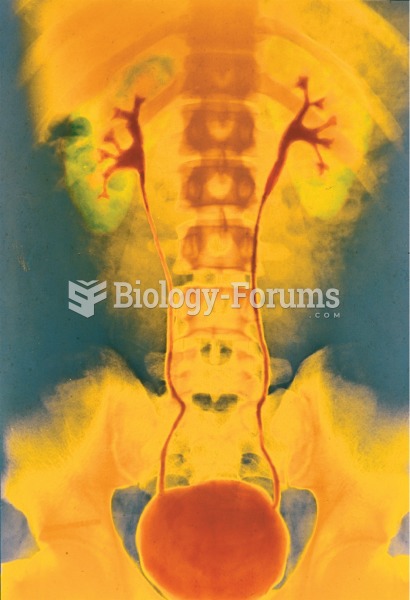
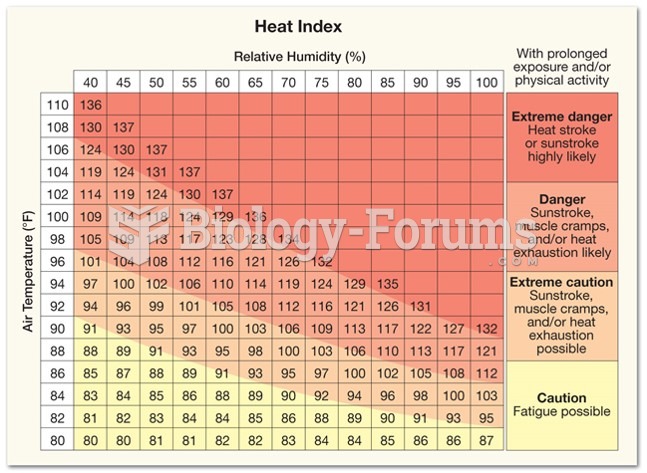
Answer to Question 1
Oceans absorb more of the available solar energy than do land surfaces at the same latitude. An ocean surface rapidly transfers heat downward by turbulent mixing and to the atmosphere above by convection. The land surface rapidly loses heat to the atmosphere by convection, but it transfers heat downward relatively slowly by conduction. Water has a high thermal conductivity, whereas land surfaces have low thermal conductivity. The heat capacity of water is about three to four times that of dry soil. Thus, the input of a given amount of energy will raise land temperatures much more than it will raise sea-surface temperatures. Differential absorption of the two surfaces is different. Whereas all the solar radiation falling on the land surface is reflected or absorbed right at the surface, some of the solar radiation falling on the ocean penetrates and is absorbed below the surface. Hence, energy is transferred downward more rapidly through water than through land.
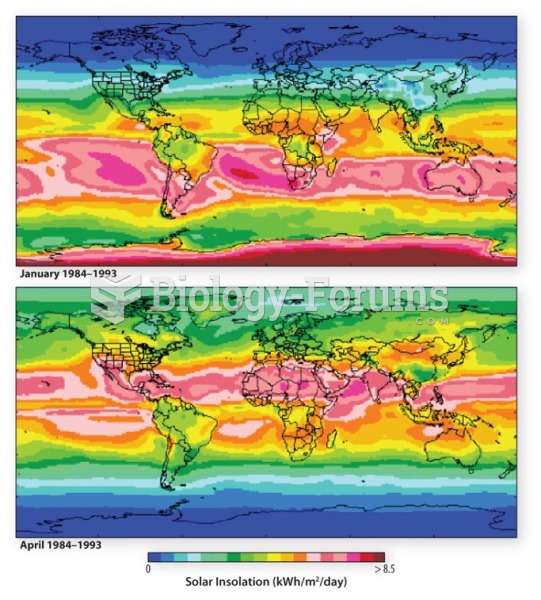
Answer to Question 2
Seasonality is caused by the tilt, or obliquity, of the Earth. The hemisphere that faces the Sun receives much more solar energy than does the other hemisphere. It is this factor that determines the seasons. For six months of each year, the Northern part of the Northern Hemisphere leans towards the Sun and the Southern part of the Southern Hemisphere leans away, leading to Summer in the Northern Hemisphere and Winter in the Southern Hemisphere. For the other six months of the year, the opposite is true. The tropics are not greatly affected by this, because the tilt of the Earth is not extreme enough to significantly reduce incoming solar radiation near the equator. There is also a difference between land and ocean. Land surfaces at all latitudes tend to experience greater seasonal variation than do ocean surfaces. Continental interiors at high latitudes, therefore, have the greatest seasonality.