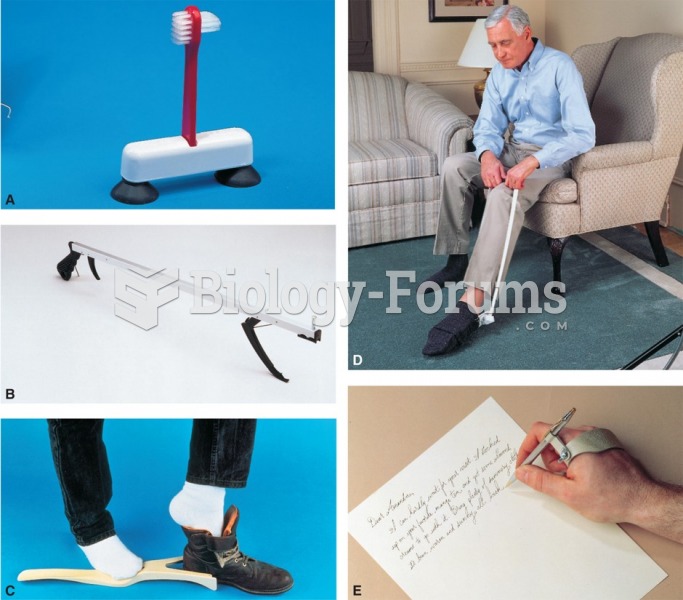
|
|
|
Interferon was scarce and expensive until 1980, when the interferon gene was inserted into bacteria using recombinant DNA technology, allowing for mass cultivation and purification from bacterial cultures.
The oldest recorded age was 122. Madame Jeanne Calment was born in France in 1875 and died in 1997. She was a vegetarian and loved olive oil, port wine, and chocolate.
More than 50% of American adults have oral herpes, which is commonly known as "cold sores" or "fever blisters." The herpes virus can be active on the skin surface without showing any signs or causing any symptoms.
An identified risk factor for osteoporosis is the intake of excessive amounts of vitamin A. Dietary intake of approximately double the recommended daily amount of vitamin A, by women, has been shown to reduce bone mineral density and increase the chances for hip fractures compared with women who consumed the recommended daily amount (or less) of vitamin A.
The most dangerous mercury compound, dimethyl mercury, is so toxic that even a few microliters spilled on the skin can cause death. Mercury has been shown to accumulate in higher amounts in the following types of fish than other types: swordfish, shark, mackerel, tilefish, crab, and tuna.
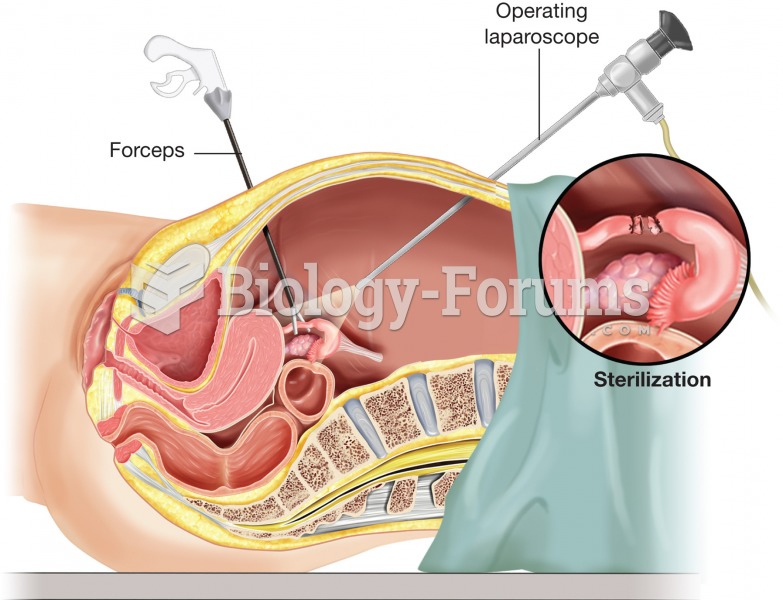 Tubal ligation. To minimize the size of the incisions necessary, laparoscopic surgery may be used to
Tubal ligation. To minimize the size of the incisions necessary, laparoscopic surgery may be used to
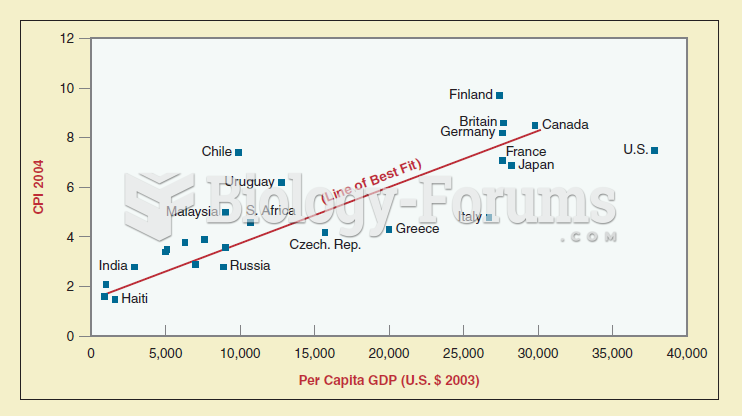 Scattergrams are a mechanism used by political scientists to show patterns and relationships among v
Scattergrams are a mechanism used by political scientists to show patterns and relationships among v