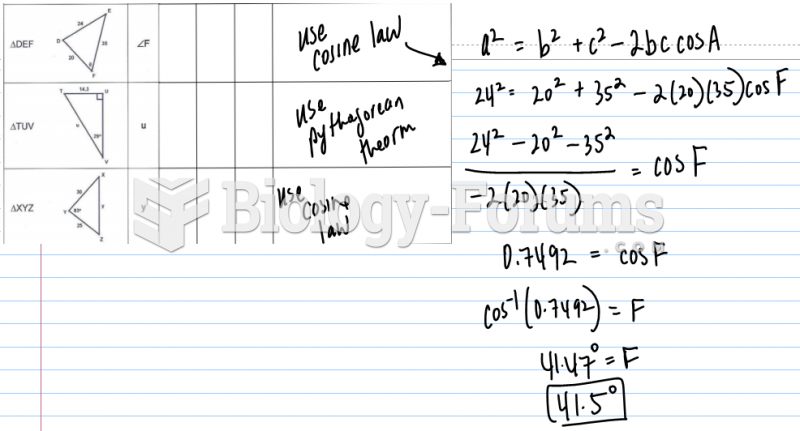
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
There are immediate benefits of chiropractic adjustments that are visible via magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). It shows that spinal manipulation therapy is effective in decreasing pain and increasing the gaps between the vertebrae, reducing pressure that leads to pain.
Did you know?
There are approximately 3 million unintended pregnancies in the United States each year.
Did you know?
On average, the stomach produces 2 L of hydrochloric acid per day.
Did you know?
By definition, when a medication is administered intravenously, its bioavailability is 100%.
Did you know?
People about to have surgery must tell their health care providers about all supplements they take.