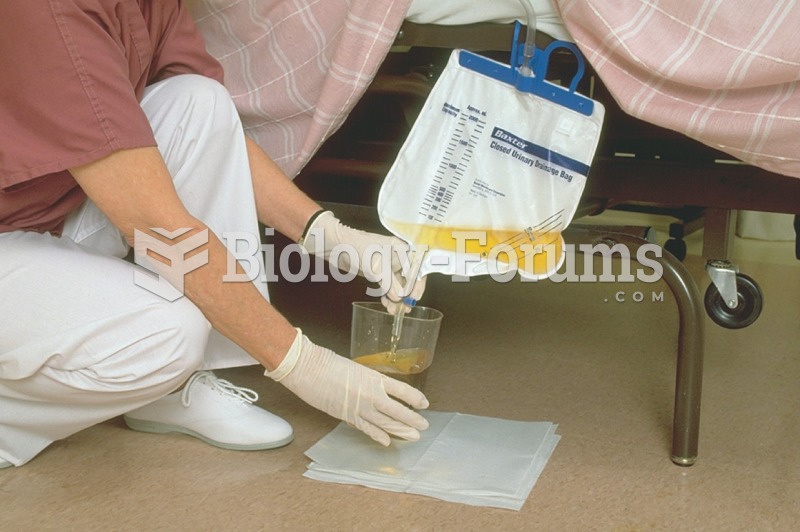
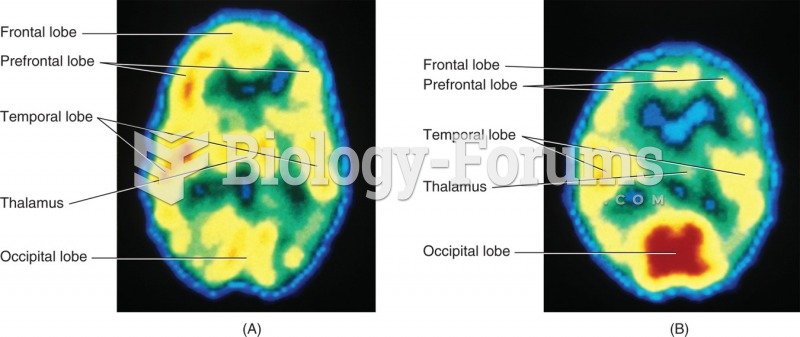
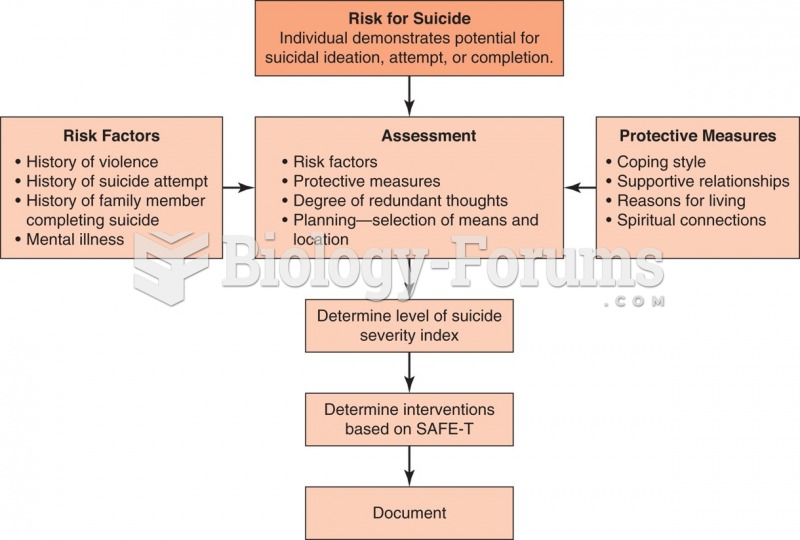
|
|
|
Approximately 25% of all reported medication errors result from some kind of name confusion.
Although not all of the following muscle groups are commonly used, intramuscular injections may be given into the abdominals, biceps, calves, deltoids, gluteals, laterals, pectorals, quadriceps, trapezoids, and triceps.
Glaucoma is a leading cause of blindness. As of yet, there is no cure. Everyone is at risk, and there may be no warning signs. It is six to eight times more common in African Americans than in whites. The best and most effective way to detect glaucoma is to receive a dilated eye examination.
Coca-Cola originally used coca leaves and caffeine from the African kola nut. It was advertised as a therapeutic agent and "pickerupper." Eventually, its formulation was changed, and the coca leaves were removed because of the effects of regulation on cocaine-related products.
The Babylonians wrote numbers in a system that used 60 as the base value rather than the number 10. They did not have a symbol for "zero."