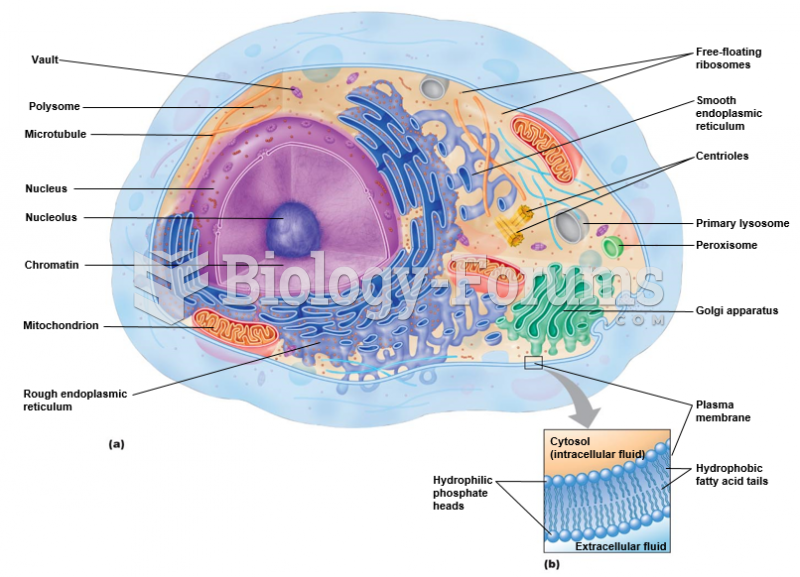
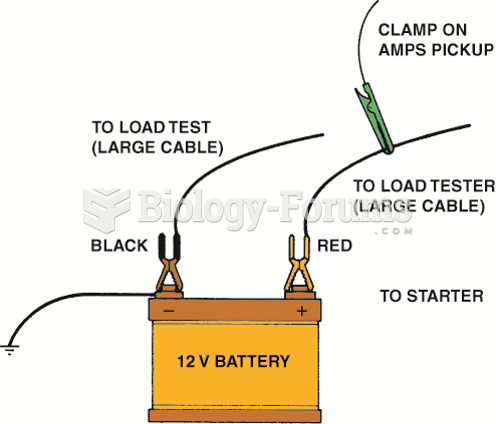
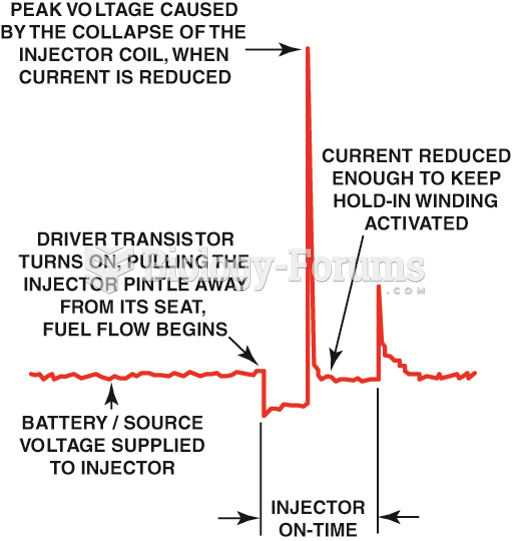
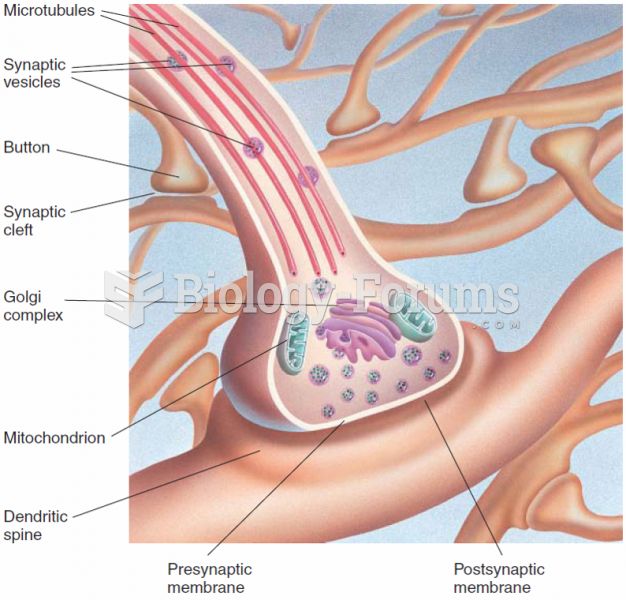
|
|
|
Long-term mental and physical effects from substance abuse include: paranoia, psychosis, immune deficiencies, and organ damage.
Elderly adults are living longer, and causes of death are shifting. At the same time, autopsy rates are at or near their lowest in history.
There are 20 feet of blood vessels in each square inch of human skin.
All patients with hyperparathyroidism will develop osteoporosis. The parathyroid glands maintain blood calcium within the normal range. All patients with this disease will continue to lose calcium from their bones every day, and there is no way to prevent the development of osteoporosis as a result.
According to the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, lung disease is the third leading killer in the United States, responsible for one in seven deaths. It is the leading cause of death among infants under the age of one year.