|
|
|
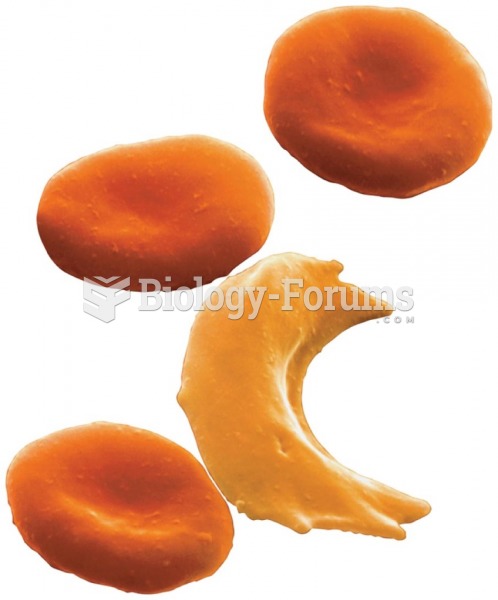
Autoimmune diseases occur when the immune system destroys its own healthy tissues. When this occurs, white blood cells cannot distinguish between pathogens and normal cells.
Patients who have undergone chemotherapy for the treatment of cancer often complain of a lack of mental focus; memory loss; and a general diminution in abilities such as multitasking, attention span, and general mental agility.
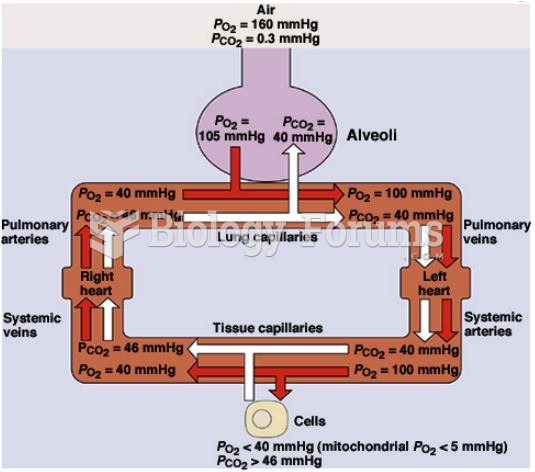
The heart is located in the center of the chest, with part of it tipped slightly so that it taps against the left side of the chest.
The human body's pharmacokinetics are quite varied. Our hair holds onto drugs longer than our urine, blood, or saliva. For example, alcohol can be detected in the hair for up to 90 days after it was consumed. The same is true for marijuana, cocaine, ecstasy, heroin, methamphetamine, and nicotine.
Human stomach acid is strong enough to dissolve small pieces of metal such as razor blades or staples.