|
|
|
Calcitonin is a naturally occurring hormone. In women who are at least 5 years beyond menopause, it slows bone loss and increases spinal bone density.
Multiple sclerosis is a condition wherein the body's nervous system is weakened by an autoimmune reaction that attacks the myelin sheaths of neurons.
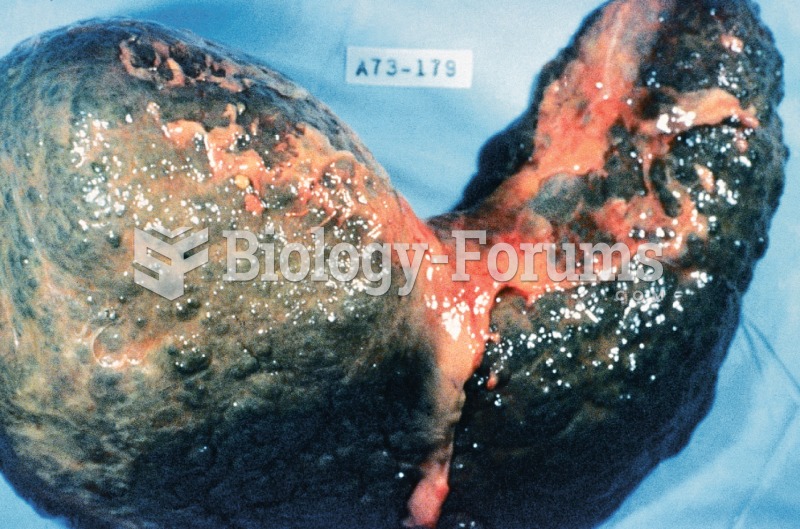
Chronic necrotizing aspergillosis has a slowly progressive process that, unlike invasive aspergillosis, does not spread to other organ systems or the blood vessels. It most often affects middle-aged and elderly individuals, spreading to surrounding tissue in the lungs. The disease often does not respond to conventionally successful treatments, and requires individualized therapies in order to keep it from becoming life-threatening.
Street names for barbiturates include reds, red devils, yellow jackets, blue heavens, Christmas trees, and rainbows. They are commonly referred to as downers.
The highest suicide rate in the United States is among people ages 65 years and older. Almost 15% of people in this age group commit suicide every year.