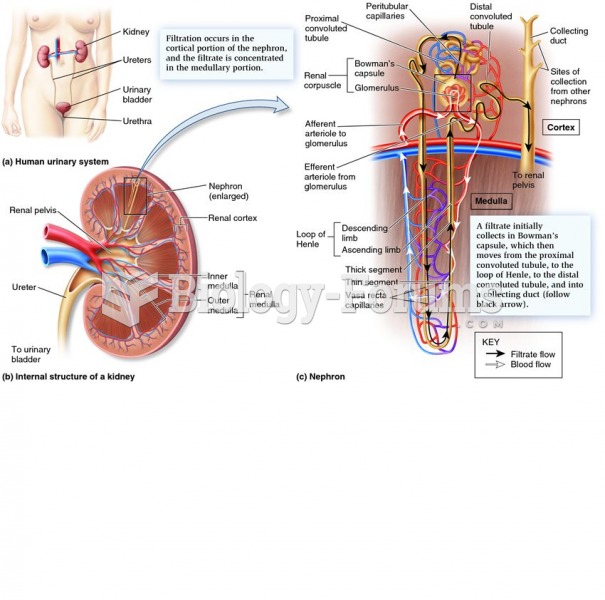
|
|
|
Fatal fungal infections may be able to resist newer antifungal drugs. Globally, fungal infections are often fatal due to the lack of access to multiple antifungals, which may be required to be utilized in combination. Single antifungals may not be enough to stop a fungal infection from causing the death of a patient.
In Eastern Europe and Russia, interferon is administered intranasally in varied doses for the common cold and influenza. It is claimed that this treatment can lower the risk of infection by as much as 60–70%.
Inotropic therapy does not have a role in the treatment of most heart failure patients. These drugs can make patients feel and function better but usually do not lengthen the predicted length of their lives.
In ancient Rome, many of the richer people in the population had lead-induced gout. The reason for this is unclear. Lead poisoning has also been linked to madness.
Adults are resistant to the bacterium that causes Botulism. These bacteria thrive in honey – therefore, honey should never be given to infants since their immune systems are not yet resistant.
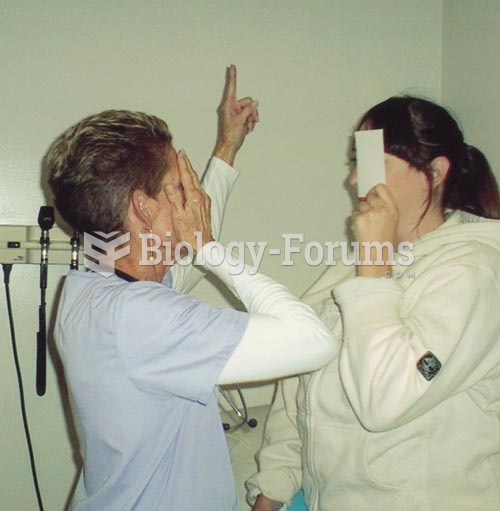 Testing Visual Fields by Confrontation: The nurse and patient should be approximately at an eye to e
Testing Visual Fields by Confrontation: The nurse and patient should be approximately at an eye to e
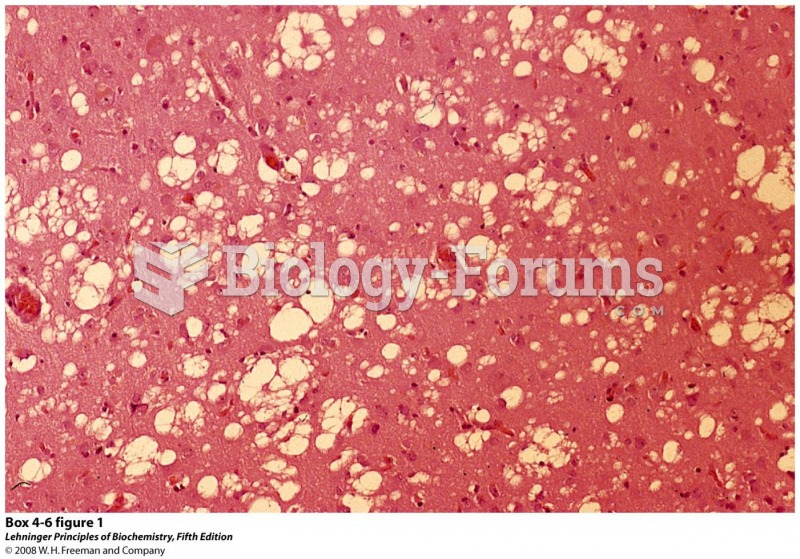
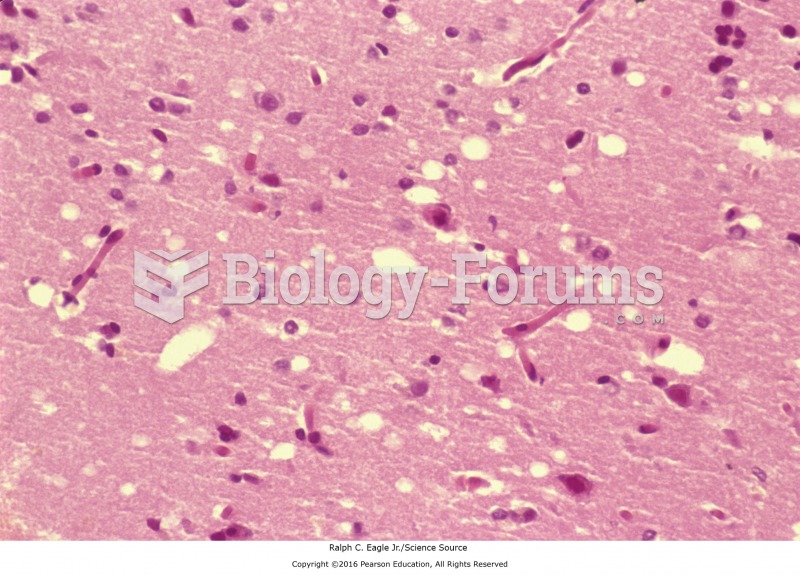 A histologic slide showing the sponge-like architecture of a patient with Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease.
A histologic slide showing the sponge-like architecture of a patient with Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease.