|
|
|
Elderly adults are living longer, and causes of death are shifting. At the same time, autopsy rates are at or near their lowest in history.
Coca-Cola originally used coca leaves and caffeine from the African kola nut. It was advertised as a therapeutic agent and "pickerupper." Eventually, its formulation was changed, and the coca leaves were removed because of the effects of regulation on cocaine-related products.
Drug-induced pharmacodynamic effects manifested in older adults include drug-induced renal toxicity, which can be a major factor when these adults are experiencing other kidney problems.
About 3.2 billion people, nearly half the world population, are at risk for malaria. In 2015, there are about 214 million malaria cases and an estimated 438,000 malaria deaths.
There are actually 60 minerals, 16 vitamins, 12 essential amino acids, and three essential fatty acids that your body needs every day.
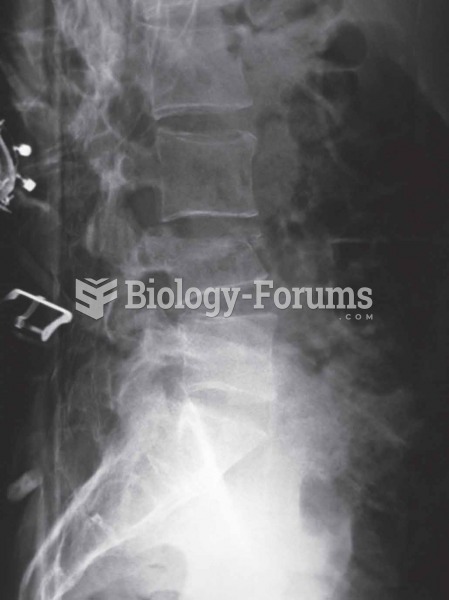 Vertebral compression Fractures of the spine (vertebra) can cause severe ”band-like” pain that radia
Vertebral compression Fractures of the spine (vertebra) can cause severe ”band-like” pain that radia
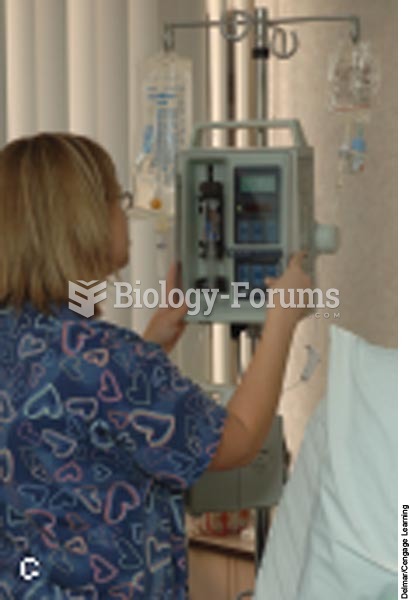 C, A nurse can also administer the medication by setting the dose and rate with an electronic infusi
C, A nurse can also administer the medication by setting the dose and rate with an electronic infusi





