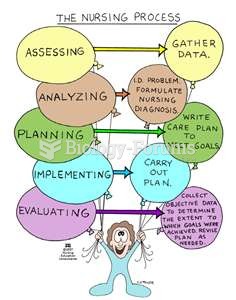
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Vaccines prevent between 2.5 and 4 million deaths every year.
Did you know?
Women are two-thirds more likely than men to develop irritable bowel syndrome. This may be attributable to hormonal changes related to their menstrual cycles.
Did you know?
Pope Sylvester II tried to introduce Arabic numbers into Europe between the years 999 and 1003, but their use did not catch on for a few more centuries, and Roman numerals continued to be the primary number system.
Did you know?
In most cases, kidneys can recover from almost complete loss of function, such as in acute kidney (renal) failure.
Did you know?
The immune system needs 9.5 hours of sleep in total darkness to recharge completely.