|
|
|
Acetaminophen (Tylenol) in overdose can seriously damage the liver. It should never be taken by people who use alcohol heavily; it can result in severe liver damage and even a condition requiring a liver transplant.
More than 20 million Americans cite use of marijuana within the past 30 days, according to the National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH). More than 8 million admit to using it almost every day.
Human kidneys will clean about 1 million gallons of blood in an average lifetime.
The U.S. Pharmacopeia Medication Errors Reporting Program states that approximately 50% of all medication errors involve insulin.
Every flu season is different, and even healthy people can get extremely sick from the flu, as well as spread it to others. The flu season can begin as early as October and last as late as May. Every person over six months of age should get an annual flu vaccine. The vaccine cannot cause you to get influenza, but in some seasons, may not be completely able to prevent you from acquiring influenza due to changes in causative viruses. The viruses in the flu shot are killed—there is no way they can give you the flu. Minor side effects include soreness, redness, or swelling where the shot was given. It is possible to develop a slight fever, and body aches, but these are simply signs that the body is responding to the vaccine and making itself ready to fight off the influenza virus should you come in contact with it.
 Acromegaly. Acromegaly is a metabolic disorder in which excessive amounts of growth hormone are secr
Acromegaly. Acromegaly is a metabolic disorder in which excessive amounts of growth hormone are secr
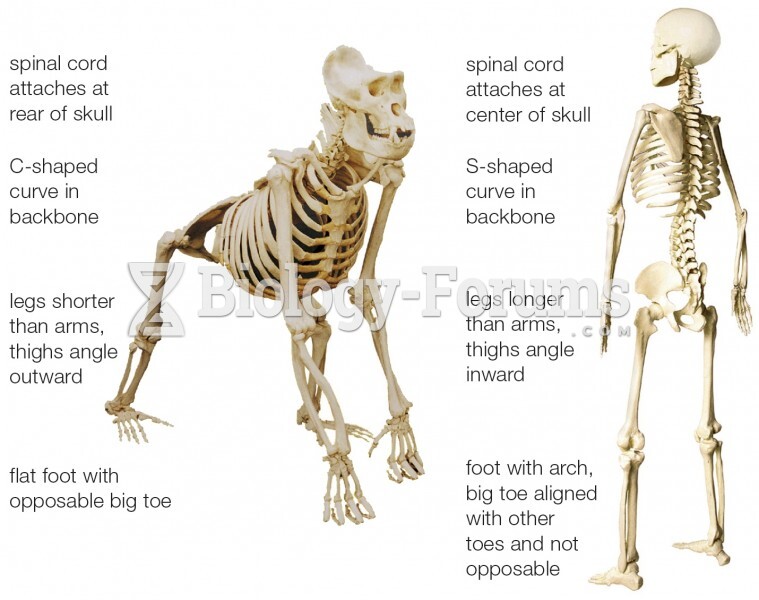
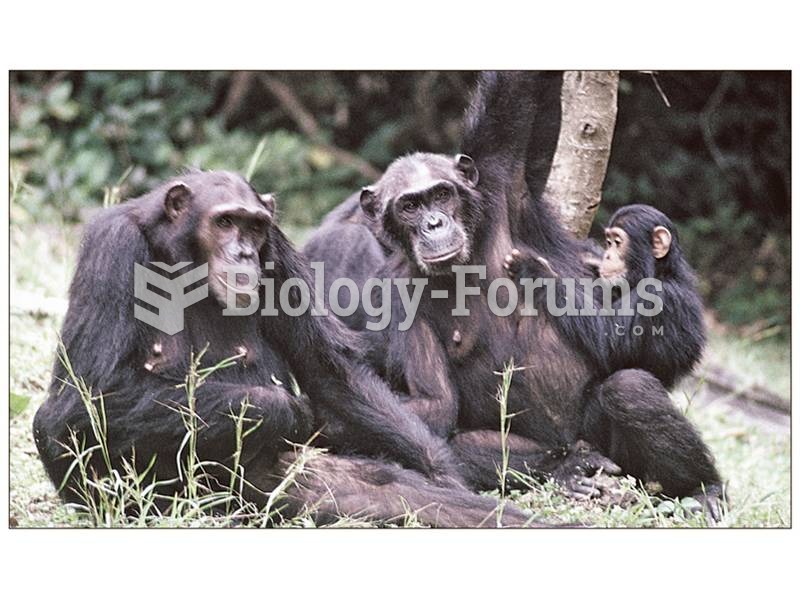 Chimpanzees live in complex kin groups in which lifelong bonds and individual personalities play key
Chimpanzees live in complex kin groups in which lifelong bonds and individual personalities play key