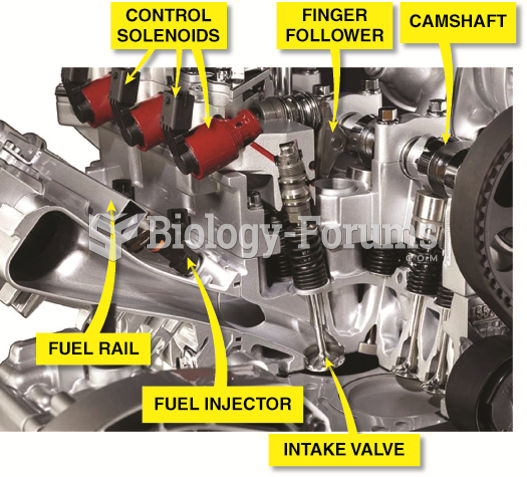
|
|
|
There are approximately 3 million unintended pregnancies in the United States each year.
During pregnancy, a woman is more likely to experience bleeding gums and nosebleeds caused by hormonal changes that increase blood flow to the mouth and nose.
Blastomycosis is often misdiagnosed, resulting in tragic outcomes. It is caused by a fungus living in moist soil, in wooded areas of the United States and Canada. If inhaled, the fungus can cause mild breathing problems that may worsen and cause serious illness and even death.
Addicts to opiates often avoid treatment because they are afraid of withdrawal. Though unpleasant, with proper management, withdrawal is rarely fatal and passes relatively quickly.
Acetaminophen (Tylenol) in overdose can seriously damage the liver. It should never be taken by people who use alcohol heavily; it can result in severe liver damage and even a condition requiring a liver transplant.
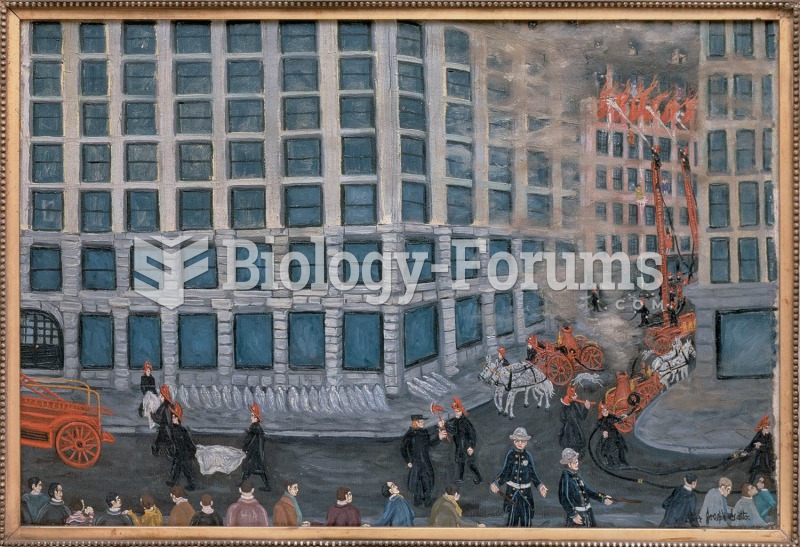 On March 25, 1911, as scores of young factory girls leaped to their deaths from the eighth, ninth, a
On March 25, 1911, as scores of young factory girls leaped to their deaths from the eighth, ninth, a
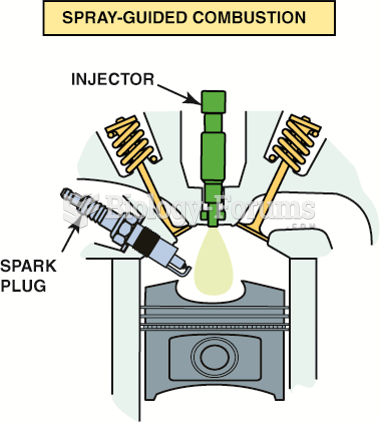 In this design, the fuel injector is at the top of the cylinder and sprays fuel into the cavity of ...
In this design, the fuel injector is at the top of the cylinder and sprays fuel into the cavity of ...