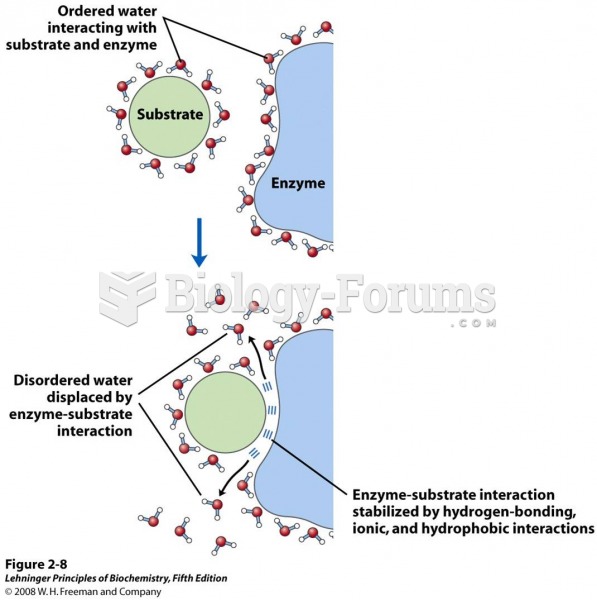
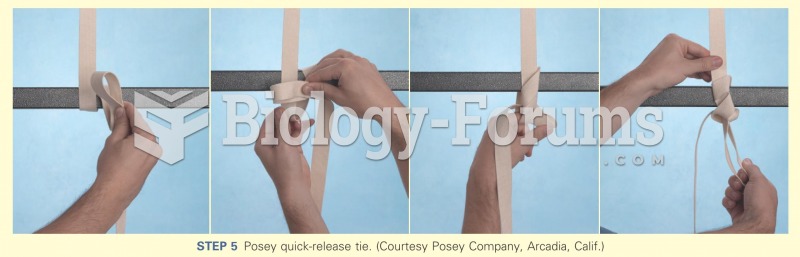
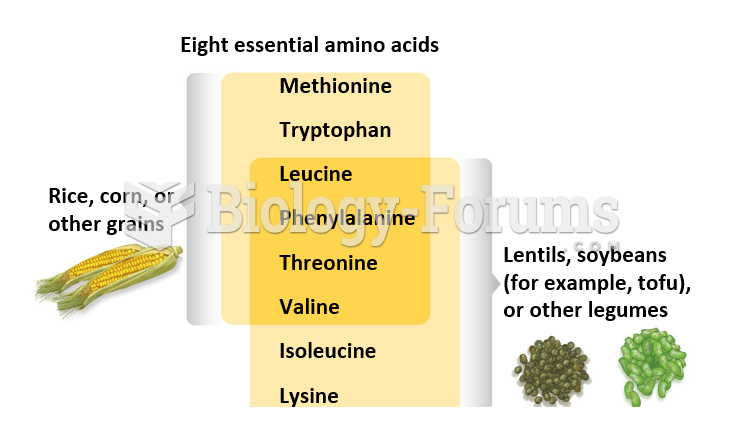
|
|
|
Vaccines cause herd immunity. If the majority of people in a community have been vaccinated against a disease, an unvaccinated person is less likely to get the disease since others are less likely to become sick from it and spread the disease.
To prove that stomach ulcers were caused by bacteria and not by stress, a researcher consumed an entire laboratory beaker full of bacterial culture. After this, he did indeed develop stomach ulcers, and won the Nobel Prize for his discovery.
The most dangerous mercury compound, dimethyl mercury, is so toxic that even a few microliters spilled on the skin can cause death. Mercury has been shown to accumulate in higher amounts in the following types of fish than other types: swordfish, shark, mackerel, tilefish, crab, and tuna.
There are 60,000 miles of blood vessels in every adult human.
Looking at the sun may not only cause headache and distort your vision temporarily, but it can also cause permanent eye damage. Any exposure to sunlight adds to the cumulative effects of ultraviolet (UV) radiation on your eyes. UV exposure has been linked to eye disorders such as macular degeneration, solar retinitis, and corneal dystrophies.