|
|
|
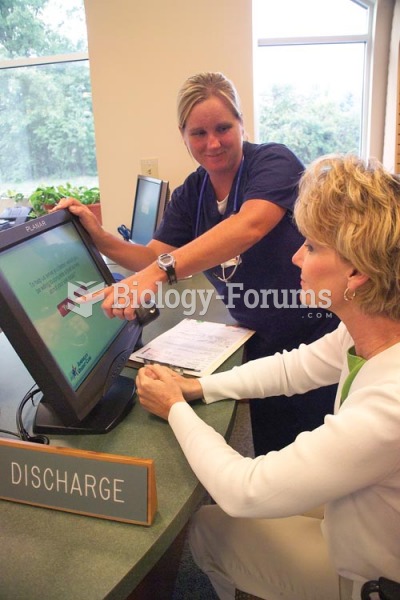
Medication errors are three times higher among children and infants than with adults.
Essential fatty acids have been shown to be effective against ulcers, asthma, dental cavities, and skin disorders such as acne.
Never take aspirin without food because it is likely to irritate your stomach. Never give aspirin to children under age 12. Overdoses of aspirin have the potential to cause deafness.
The Babylonians wrote numbers in a system that used 60 as the base value rather than the number 10. They did not have a symbol for "zero."
GI conditions that will keep you out of the U.S. armed services include ulcers, varices, fistulas, esophagitis, gastritis, congenital abnormalities, inflammatory bowel disease, enteritis, colitis, proctitis, duodenal diverticula, malabsorption syndromes, hepatitis, cirrhosis, cysts, abscesses, pancreatitis, polyps, certain hemorrhoids, splenomegaly, hernias, recent abdominal surgery, GI bypass or stomach stapling, and artificial GI openings.