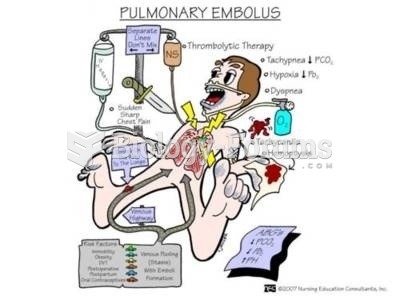
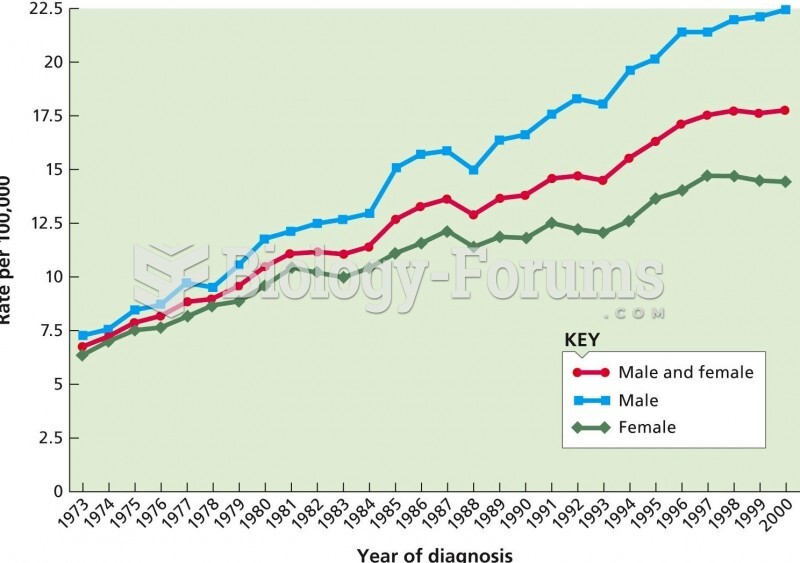
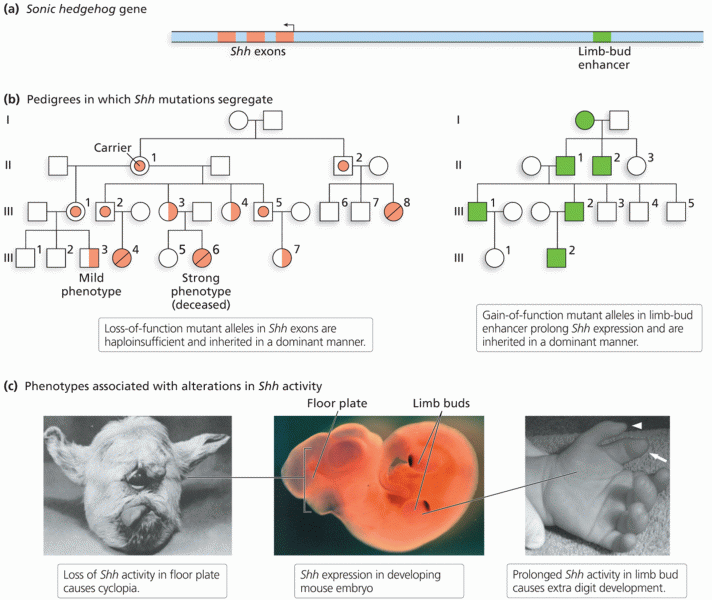
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Carbamazepine can interfere with the results of home pregnancy tests. If you are taking carbamazepine, do not try to test for pregnancy at home.
Did you know?
The longest a person has survived after a heart transplant is 24 years.
Did you know?
More than one-third of adult Americans are obese. Diseases that kill the largest number of people annually, such as heart disease, cancer, diabetes, stroke, and hypertension, can be attributed to diet.
Did you know?
Alcohol acts as a diuretic. Eight ounces of water is needed to metabolize just 1 ounce of alcohol.
Did you know?
In the United States, an estimated 50 million unnecessary antibiotics are prescribed for viral respiratory infections.