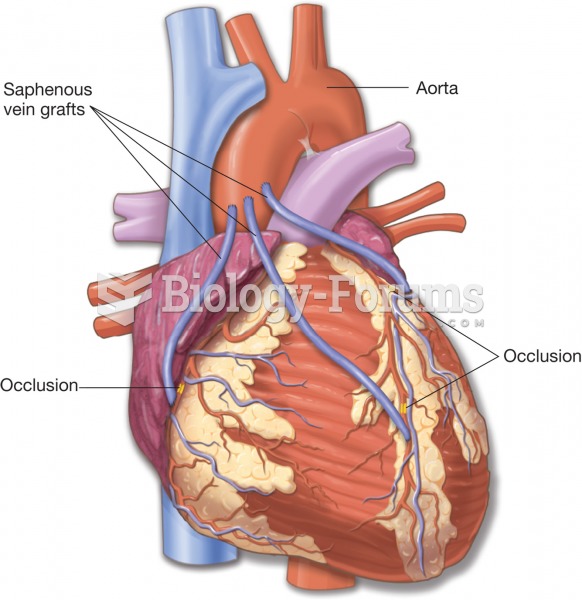
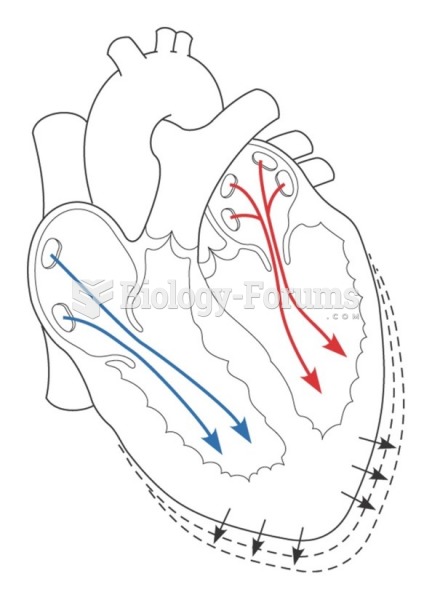
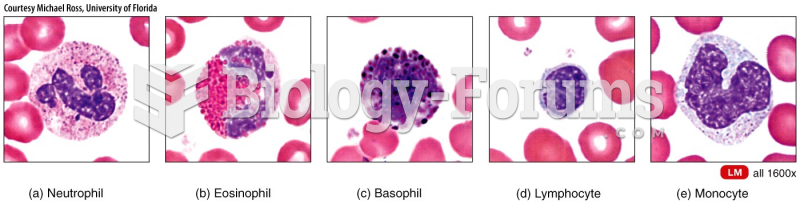
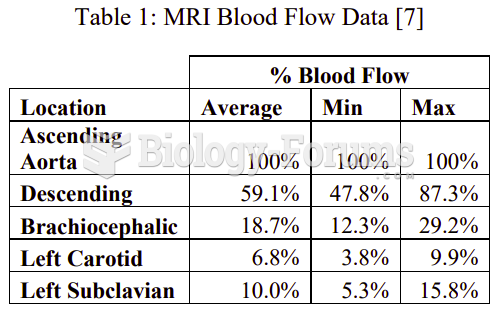
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
In 1844, Charles Goodyear obtained the first patent for a rubber condom.
Did you know?
After 5 years of being diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis, one every three patients will no longer be able to work.
Did you know?
Your chance of developing a kidney stone is 1 in 10. In recent years, approximately 3.7 million people in the United States were diagnosed with a kidney disease.
Did you know?
Approximately 15–25% of recognized pregnancies end in miscarriage. However, many miscarriages often occur before a woman even knows she is pregnant.
Did you know?
Calcitonin is a naturally occurring hormone. In women who are at least 5 years beyond menopause, it slows bone loss and increases spinal bone density.