|
|
|
Never take aspirin without food because it is likely to irritate your stomach. Never give aspirin to children under age 12. Overdoses of aspirin have the potential to cause deafness.
Human neurons are so small that they require a microscope in order to be seen. However, some neurons can be up to 3 feet long, such as those that extend from the spinal cord to the toes.
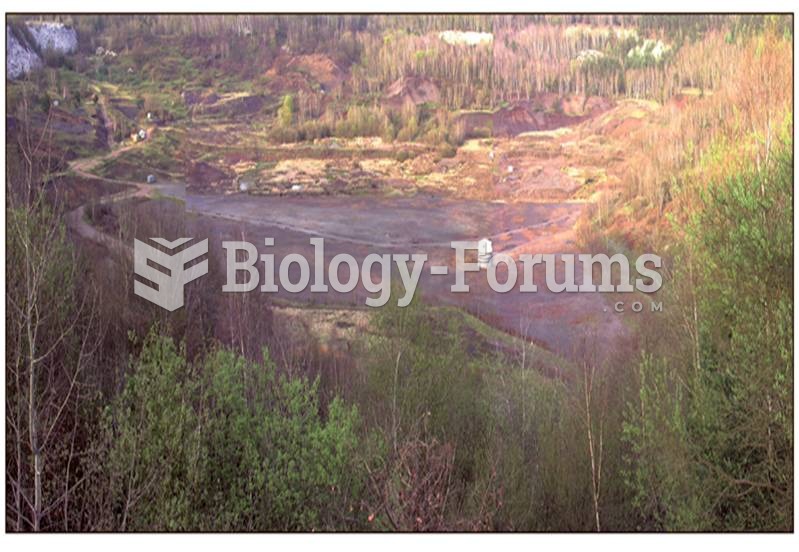
Blastomycosis is often misdiagnosed, resulting in tragic outcomes. It is caused by a fungus living in moist soil, in wooded areas of the United States and Canada. If inhaled, the fungus can cause mild breathing problems that may worsen and cause serious illness and even death.
The top 10 most important tips that will help you grow old gracefully include (1) quit smoking, (2) keep your weight down, (3) take supplements, (4) skip a meal each day or fast 1 day per week, (5) get a pet, (6) get medical help for chronic pain, (7) walk regularly, (8) reduce arguments, (9) put live plants in your living space, and (10) do some weight training.
The types of cancer that alpha interferons are used to treat include hairy cell leukemia, melanoma, follicular non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, and AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma.