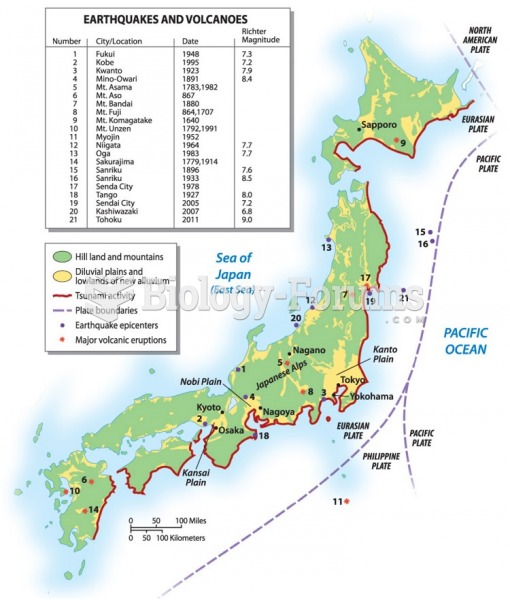
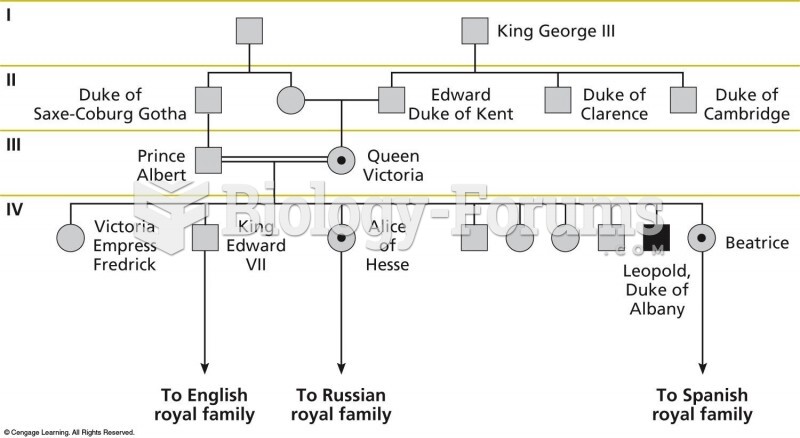
|
|
|
Allergies play a major part in the health of children. The most prevalent childhood allergies are milk, egg, soy, wheat, peanuts, tree nuts, and seafood.
Today, nearly 8 out of 10 pregnant women living with HIV (about 1.1 million), receive antiretrovirals.
Always store hazardous household chemicals in their original containers out of reach of children. These include bleach, paint, strippers and products containing turpentine, garden chemicals, oven cleaners, fondue fuels, nail polish, and nail polish remover.
There are more nerve cells in one human brain than there are stars in the Milky Way.
Certain rare plants containing cyanide include apricot pits and a type of potato called cassava. Fortunately, only chronic or massive ingestion of any of these plants can lead to serious poisoning.