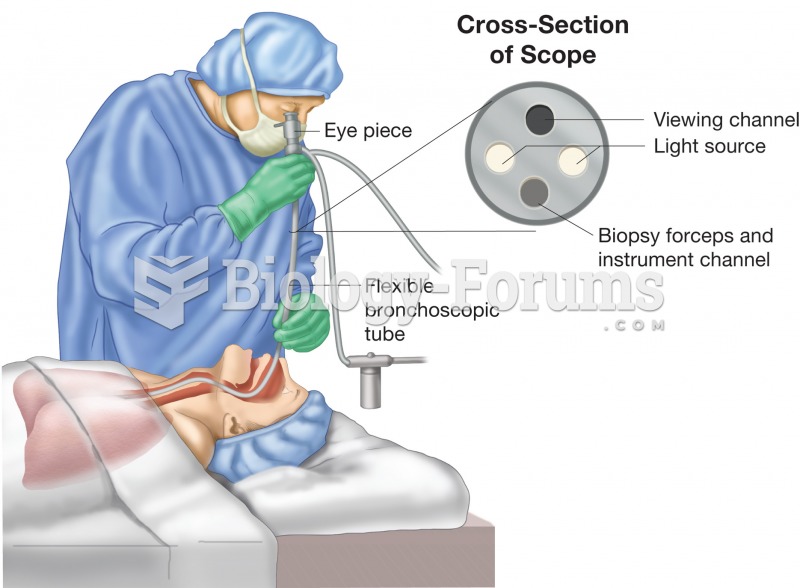
|
|
|
People who have myopia, or nearsightedness, are not able to see objects at a distance but only up close. It occurs when the cornea is either curved too steeply, the eye is too long, or both. This condition is progressive and worsens with time. More than 100 million people in the United States are nearsighted, but only 20% of those are born with the condition. Diet, eye exercise, drug therapy, and corrective lenses can all help manage nearsightedness.
There are 20 feet of blood vessels in each square inch of human skin.
Asthma-like symptoms were first recorded about 3,500 years ago in Egypt. The first manuscript specifically written about asthma was in the year 1190, describing a condition characterized by sudden breathlessness. The treatments listed in this manuscript include chicken soup, herbs, and sexual abstinence.
More than 150,000 Americans killed by cardiovascular disease are younger than the age of 65 years.
Asthma is the most common chronic childhood disease in the world. Most children who develop asthma have symptoms before they are 5 years old.