|
|
|
The average person is easily confused by the terms pharmaceutics and pharmacology, thinking they are one and the same. Whereas pharmaceutics is the science of preparing and dispensing drugs (otherwise known as the science of pharmacy), pharmacology is the study of medications.
In most cases, kidneys can recover from almost complete loss of function, such as in acute kidney (renal) failure.
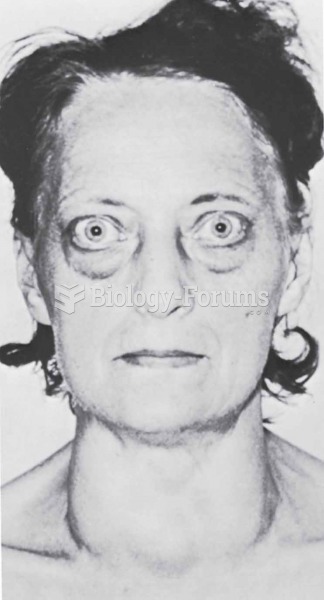
The toxic levels for lithium carbonate are close to the therapeutic levels. Signs of toxicity include fine hand tremor, polyuria, mild thirst, nausea, general discomfort, diarrhea, vomiting, drowsiness, muscular weakness, lack of coordination, ataxia, giddiness, tinnitus, and blurred vision.
Cytomegalovirus affects nearly the same amount of newborns every year as Down syndrome.
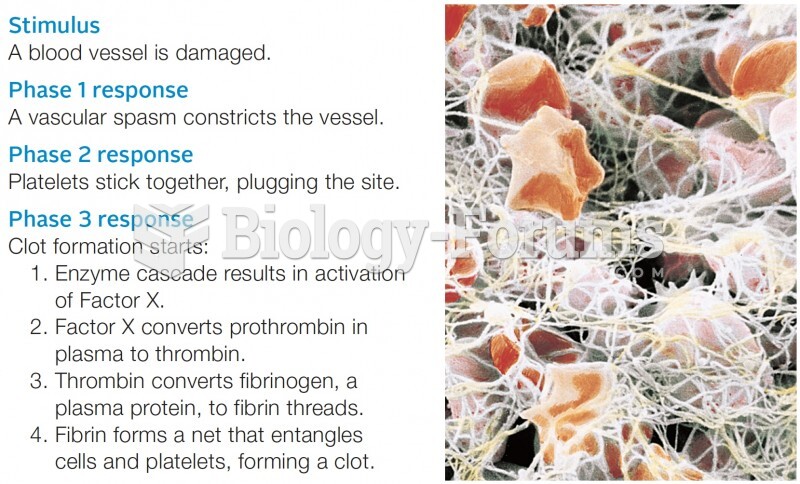
Most strokes are caused when blood clots move to a blood vessel in the brain and block blood flow to that area. Thrombolytic therapy can be used to dissolve the clot quickly. If given within 3 hours of the first stroke symptoms, this therapy can help limit stroke damage and disability.