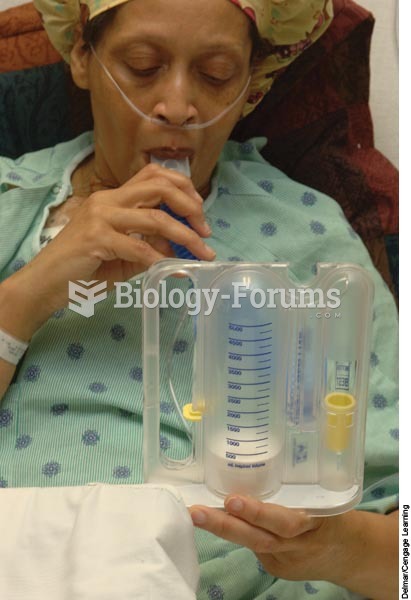
|
|
|
Persons who overdose with cardiac glycosides have a better chance of overall survival if they can survive the first 24 hours after the overdose.
Not getting enough sleep can greatly weaken the immune system. Lack of sleep makes you more likely to catch a cold, or more difficult to fight off an infection.
A good example of polar molecules can be understood when trying to make a cake. If water and oil are required, they will not mix together. If you put them into a measuring cup, the oil will rise to the top while the water remains on the bottom.
Essential fatty acids have been shown to be effective against ulcers, asthma, dental cavities, and skin disorders such as acne.
Autoimmune diseases occur when the immune system destroys its own healthy tissues. When this occurs, white blood cells cannot distinguish between pathogens and normal cells.
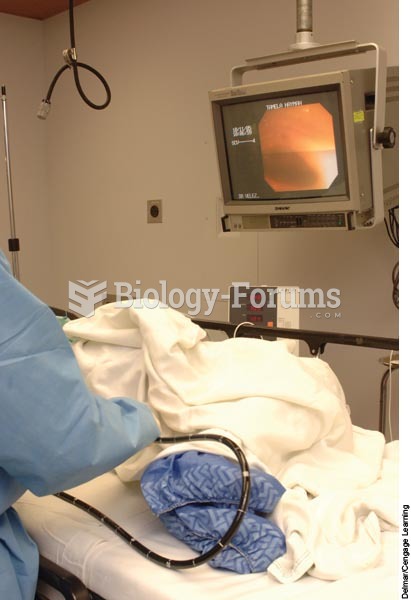 A physician is performing a colonoscopy on a client and viewing the internal structures of the colon
A physician is performing a colonoscopy on a client and viewing the internal structures of the colon
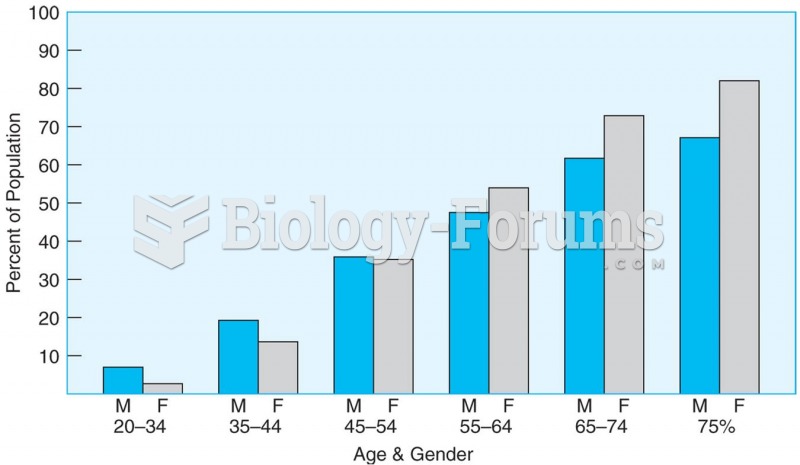 The proportion of men and women with elevated blood pressure or taking hypertension medication incre
The proportion of men and women with elevated blood pressure or taking hypertension medication incre