Answer to Question 1
1,3
Rationale 1: It is recommended that this product be patch-tested on a small area of skin for 3 days to determine if the patient is allergic to its ingredients.
Rationale 2: Worsening of the acne is not the priority information.
Rationale 3: Rare, but potentially life-threatening, allergic reactions have occurred with use of this medication.
Rationale 4: Most products require gentle face-washing prior to application, but this is not the priority information.
Rationale 5: There is no reason to avoid aspirin when taking this medication.
Global Rationale: It is recommended that this product be patch-tested on a small area of skin for 3 days to determine if the patient is allergic to its ingredients. Rare, but potentially life-threatening, allergic reactions have occurred with use of this medication. Worsening of the acne is not the priority information. Most products require gentle face-washing prior to application, but this is not the priority information. There is no reason to avoid aspirin when taking this medication.
Answer to Question 2
3
Rationale 1:The goal of general anesthesia is to provide a rapid and complete loss of sensation.
Rationale 2:General anesthesia is the loss of sensation to the entire body.
Rationale 3: The goal of general anesthesia is to provide a rapid and complete loss of sensation. Signs of general anesthesia include total analgesia (no feeling of pain) and loss of consciousness, memory, and body movement. Although these signs are similar to those of sleeping, general anesthesia and sleep are not exactly the same. General anesthetics stop all nervous activity in the brain, whereas sleeping stops activity in only very specific areas. In fact, some brain activity actually increases during sleep.
Rationale 4:The goal of general anesthesia is to provide a rapid and complete loss of sensation and loss of consciousness, memory, and body movement.
Global Rationale: The goal of general anesthesia is to provide a rapid and complete loss of sensation. Signs of general anesthesia include total analgesia (no feeling of pain) and loss of consciousness, memory, and body movement. Although these signs are similar to those of sleeping, general anesthesia and sleep are not exactly the same. General anesthetics stop all nervous activity in the brain, whereas sleeping stops activity in only very specific areas. In fact, some brain activity actually increases during sleep.
 When working with the patient with impaired hearing, the interpreter needs to direct questions to th
When working with the patient with impaired hearing, the interpreter needs to direct questions to th
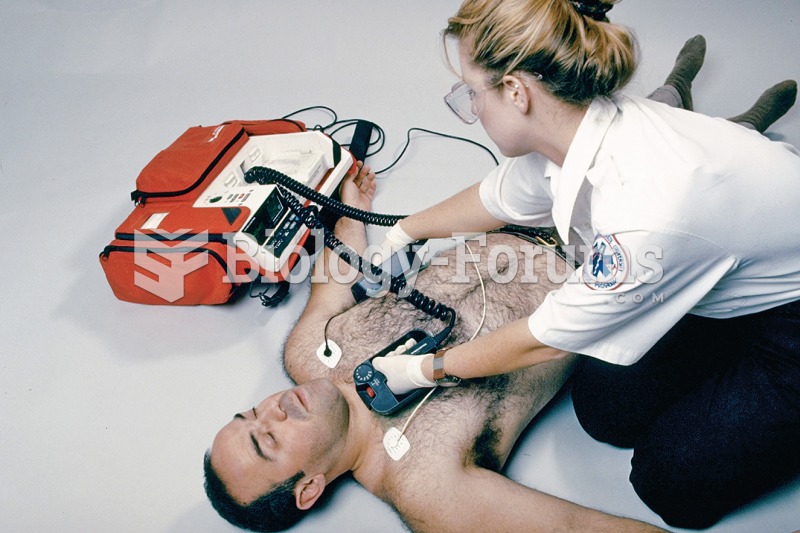 An emergency medical technician positions defibrillator paddles on the chest of a supine male patien
An emergency medical technician positions defibrillator paddles on the chest of a supine male patien