|
|
|
Every flu season is different, and even healthy people can get extremely sick from the flu, as well as spread it to others. The flu season can begin as early as October and last as late as May. Every person over six months of age should get an annual flu vaccine. The vaccine cannot cause you to get influenza, but in some seasons, may not be completely able to prevent you from acquiring influenza due to changes in causative viruses. The viruses in the flu shot are killed—there is no way they can give you the flu. Minor side effects include soreness, redness, or swelling where the shot was given. It is possible to develop a slight fever, and body aches, but these are simply signs that the body is responding to the vaccine and making itself ready to fight off the influenza virus should you come in contact with it.
Today, nearly 8 out of 10 pregnant women living with HIV (about 1.1 million), receive antiretrovirals.
Certain chemicals, after ingestion, can be converted by the body into cyanide. Most of these chemicals have been removed from the market, but some old nail polish remover, solvents, and plastics manufacturing solutions can contain these substances.
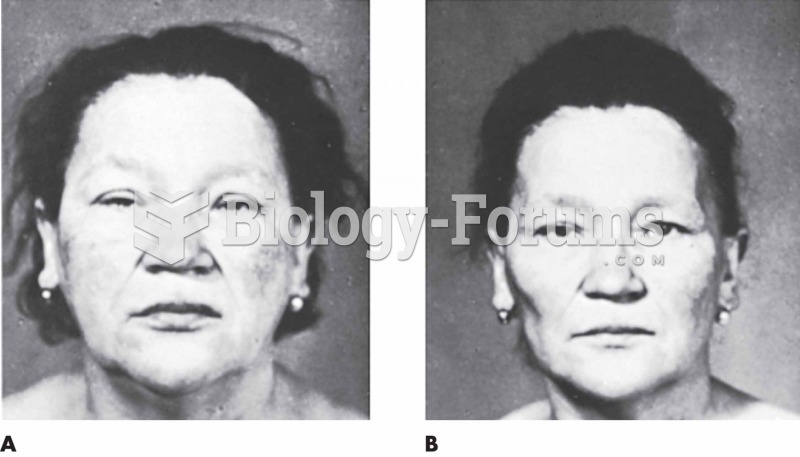
Hyperthyroidism leads to an increased rate of metabolism and affects about 1% of women but only 0.1% of men. For most people, this increased metabolic rate causes the thyroid gland to become enlarged (known as a goiter).
People with alcoholism are at a much greater risk of malnutrition than are other people and usually exhibit low levels of most vitamins (especially folic acid). This is because alcohol often takes the place of 50% of their daily intake of calories, with little nutritional value contained in it.