|
|
|
Many people have small pouches in their colons that bulge outward through weak spots. Each pouch is called a diverticulum. About 10% of Americans older than age 40 years have diverticulosis, which, when the pouches become infected or inflamed, is called diverticulitis. The main cause of diverticular disease is a low-fiber diet.
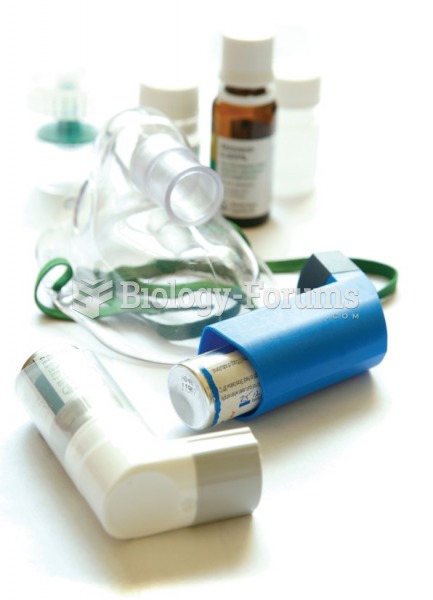
Asthma-like symptoms were first recorded about 3,500 years ago in Egypt. The first manuscript specifically written about asthma was in the year 1190, describing a condition characterized by sudden breathlessness. The treatments listed in this manuscript include chicken soup, herbs, and sexual abstinence.
In the United States, congenital cytomegalovirus causes one child to become disabled almost every hour. CMV is the leading preventable viral cause of development disability in newborns. These disabilities include hearing or vision loss, and cerebral palsy.
Most women experience menopause in their 50s. However, in 1994, an Italian woman gave birth to a baby boy when she was 61 years old.
Illicit drug use costs the United States approximately $181 billion every year.