Answer to Question 1
Correct Answer: 1,2,3,4
Rationale 1: It is more effective and less expensive to administer pituitary hormones rather than hypothalamic hormones when the hypothalamus is malfunctioning. Thyroid hormone may be prescribed for this client.
Rationale 2: It is more effective and less expensive to administer pituitary hormones rather than hypothalamic hormones when the hypothalamus is malfunctioning. Corticosteroids may be prescribed for this client.
Rationale 3: It is more effective and less expensive to administer pituitary hormones rather than hypothalamic hormones when the hypothalamus is malfunctioning. Estrogen may be prescribed for this client.
Rationale 4: It is more effective and less expensive to administer pituitary hormones rather than hypothalamic hormones when the hypothalamus is malfunctioning. Progesterone may be prescribed for this client.
Rationale 5: Initially the effect of the GnRH analogs is to increase the production of interstitial cell-stimulating hormone (in males) or follicle-stimulating hormone (in females), which increases the secretion of sex hormones. With continued therapy, however, the pituitary becomes insensitive to the effects of GnRH, and the production of sex hormones falls to near castration levels.
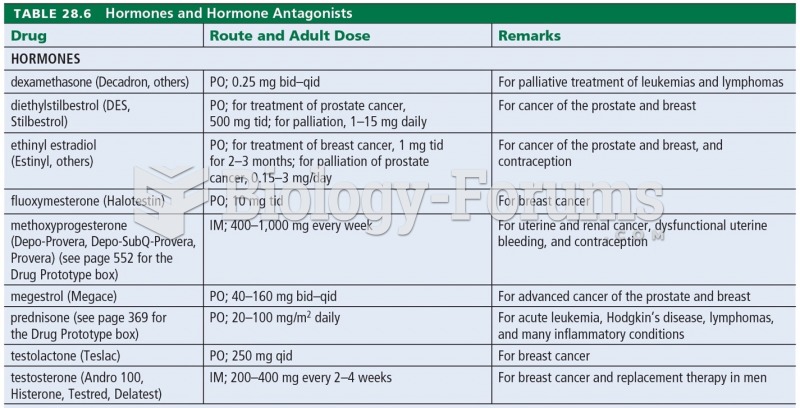
Global Rationale: It is more effective and less expensive to administer pituitary hormones rather than hypothalamic hormones when the hypothalamus is malfunctioning. Thyroid hormone, estrogen, corticosteroids, and progesterone may be prescribed for this client. Initially the effect of the GnRH analogs is to increase the production of interstitial cell-stimulating hormone (in males) or follicle-stimulating hormone (in females), which increases the secretion of sex hormones. With continued therapy, however, the pituitary becomes insensitive to the effects of GnRH, and the production of sex hormones falls to near castration levels.
Answer to Question 2
Correct Answer: 0.6
Rationale: The client weighs 44 lbs. To determine kilograms, divide 44 lbs by 2.2. The client weighs 20 kg. Multiply the weekly dose of 0.21 mg by 20. The client should receive 4.2 mg of the medication every week. To determine the daily dose, divide the weekly dose of 4.2 by 7, for 7 days, to calculate that the client is to receive 0.6 mg of the medication every day.
Global Rationale: The client weighs 44 lbs. To determine kilograms, divide 44 lbs by 2.2. The client weighs 20 kg. Multiply the weekly dose of 0.21 mg by 20. The client should receive 4.2 mg of the medication every week. To determine the daily dose, divide the weekly dose of 4.2 by 7, for 7 days, to calculate that the client is to receive 0.6 mg of the medication every day.