|
|
|
Drying your hands with a paper towel will reduce the bacterial count on your hands by 45–60%.
Looking at the sun may not only cause headache and distort your vision temporarily, but it can also cause permanent eye damage. Any exposure to sunlight adds to the cumulative effects of ultraviolet (UV) radiation on your eyes. UV exposure has been linked to eye disorders such as macular degeneration, solar retinitis, and corneal dystrophies.
Asthma attacks and symptoms usually get started by specific triggers (such as viruses, allergies, gases, and air particles). You should talk to your doctor about these triggers and find ways to avoid or get rid of them.
Disorders that may affect pharmacodynamics include genetic mutations, malnutrition, thyrotoxicosis, myasthenia gravis, Parkinson's disease, and certain forms of insulin-resistant diabetes mellitus.
The most common treatment options for addiction include psychotherapy, support groups, and individual counseling.
 Preschool and child care afford opportunities for many new experiences but also can be stressful for ...
Preschool and child care afford opportunities for many new experiences but also can be stressful for ...
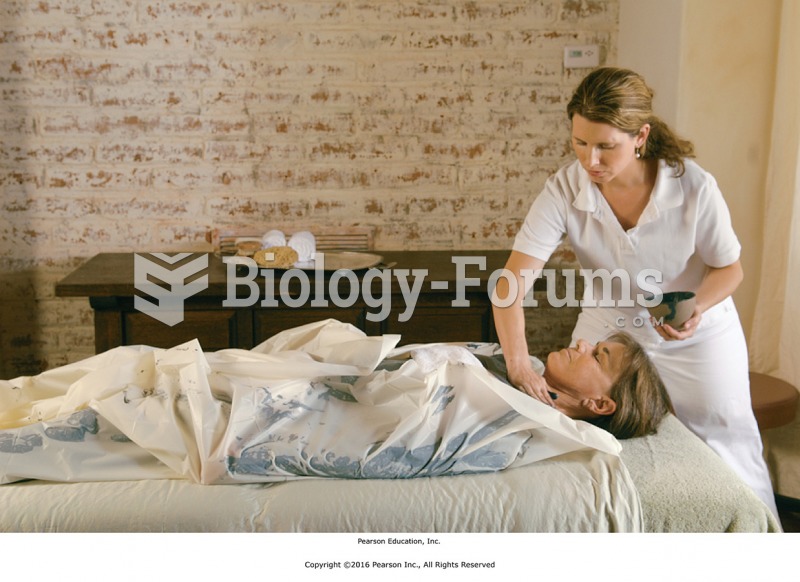
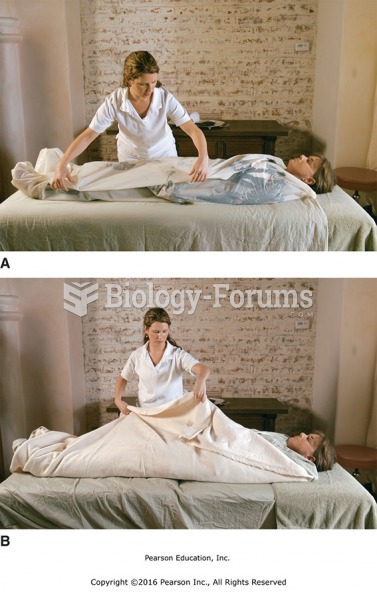 Wrap the client securely with sheets. (A) Lay one side of the sheet over the body. (B) Enclose the ...
Wrap the client securely with sheets. (A) Lay one side of the sheet over the body. (B) Enclose the ...