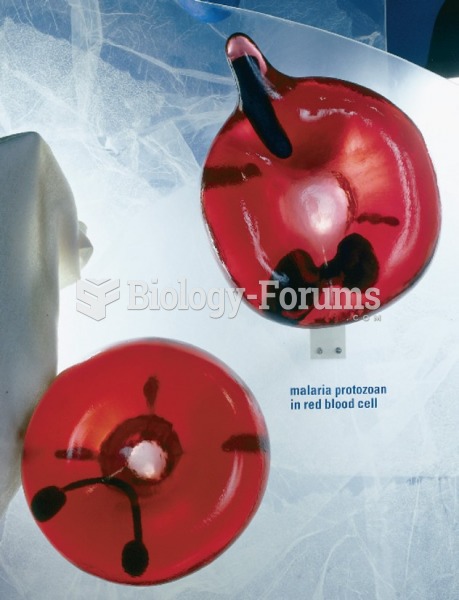
|
|
|
Persons who overdose with cardiac glycosides have a better chance of overall survival if they can survive the first 24 hours after the overdose.
Of the estimated 2 million heroin users in the United States, 600,000–800,000 are considered hardcore addicts. Heroin addiction is considered to be one of the hardest addictions to recover from.
In women, pharmacodynamic differences include increased sensitivity to (and increased effectiveness of) beta-blockers, opioids, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, and typical antipsychotics.
The tallest man ever known was Robert Wadlow, an American, who reached the height of 8 feet 11 inches. He died at age 26 years from an infection caused by the immense weight of his body (491 pounds) and the stress on his leg bones and muscles.
Individuals are never “cured” of addictions. Instead, they learn how to manage their disease to lead healthy, balanced lives.
 A guinea pig being examined by a veterinary medical officer for general health and pulmonary conditi
A guinea pig being examined by a veterinary medical officer for general health and pulmonary conditi
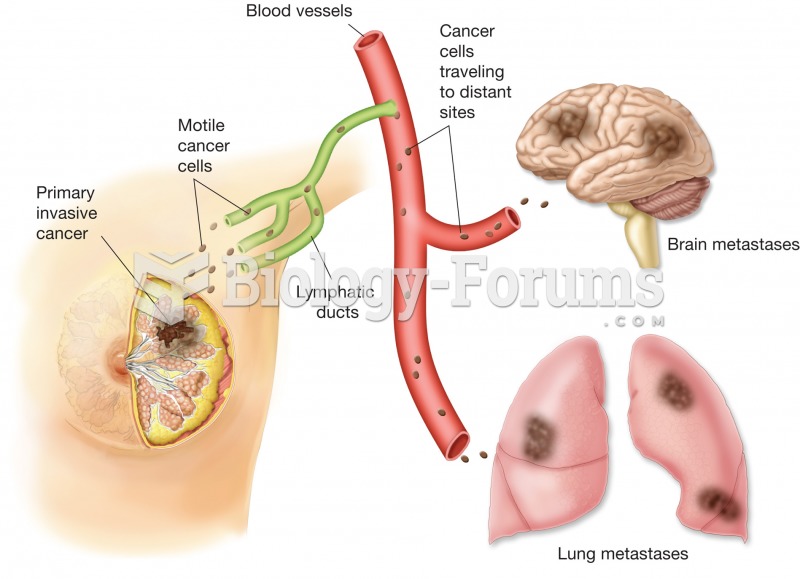 Illustration showing how the primary breast tumor metastasized through the lymphatic and blood vesse
Illustration showing how the primary breast tumor metastasized through the lymphatic and blood vesse