|
|
|
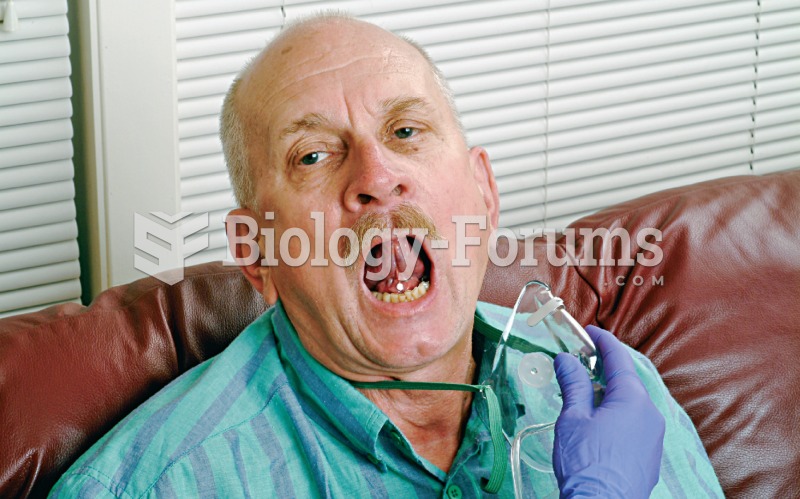
The Food and Drug Administration has approved Risperdal, an adult antipsychotic drug, for the symptomatic treatment of irritability in children and adolescents with autism. The approval is the first for the use of a drug to treat behaviors associated with autism in children. These behaviors are included under the general heading of irritability and include aggression, deliberate self-injury, and temper tantrums.
There used to be a metric calendar, as well as metric clocks. The metric calendar, or "French Republican Calendar" divided the year into 12 months, but each month was divided into three 10-day weeks. Each day had 10 decimal hours. Each hour had 100 decimal minutes. Due to lack of popularity, the metric clocks and calendars were ended in 1795, three years after they had been first marketed.
Each year in the United States, there are approximately six million pregnancies. This means that at any one time, about 4% of women in the United States are pregnant.
The liver is the only organ that has the ability to regenerate itself after certain types of damage. As much as 25% of the liver can be removed, and it will still regenerate back to its original shape and size. However, the liver cannot regenerate after severe damage caused by alcohol.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) was originally known as the Communicable Disease Center, which was formed to fight malaria. It was originally headquartered in Atlanta, Georgia, since the Southern states faced the worst threat from malaria.