Answer to Question 1
Correct Answer: 1,2,3,4
Rationale 1: This medication has been proven to extend survival by reducing the degeneration of neurons.
Rationale 2: It is a tablet that should be taken every 12 hours on an empty stomach.
Rationale 3: The client should avoid high-fat meals before or after taking the medication because fat interferes with medication absorption.
Rationale 4: Common adverse effects include headache and dizziness.
Rationale 5: Paralytic ileus is not a life-threatening adverse effect of this medication.
Global Rationale: This medication has been proven to extend survival by reducing the degeneration of neurons. It is a tablet that should be taken every 12 hours on an empty stomach. The client should avoid high-fat meals before or after taking the medication because fat interferes with medication absorption. Common adverse effects include headache and dizziness. Paralytic ileus is not a life-threatening adverse effect of this medication.
Answer to Question 2
Correct Answer: 1,2,3,4,5,6
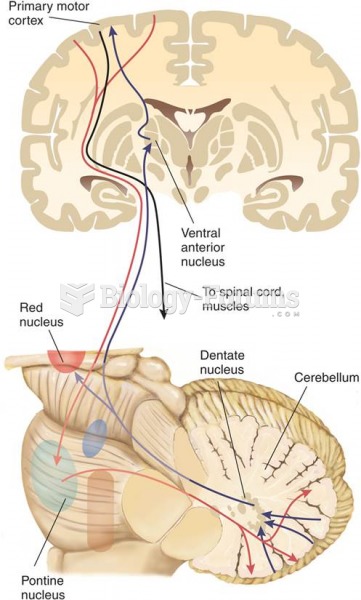
Rationale 1: The substantia nigra, a dark band of gray matter in the midbrain, is a primary producer of the neurotransmitter dopamine.
Rationale 2: The dopamine travels through axons along the nigrostriatal pathway to the corpus striatum.
Rationale 3: When dopamine reaches the nigrostriatal pathways, it is released.
Rationale 4: In the corpus striatum, dopamine encounters its receptors and produces multiple actions.
Rationale 5: Dopamine serves an inhibitory function, slowing the flow of impulses down spinal neurons.
Rationale 6: When dopamine is present, the normal flow of motor impulses from the corpus striatum helps to produce coordinated unconscious muscle movement.
Global Rationale: The substantia nigra, a dark band of gray matter in the midbrain, is a primary producer of the neurotransmitter dopamine. The dopamine travels through axons along the nigrostriatal pathway to the corpus striatum. When dopamine reaches the nigrostriatal pathways, it is released. In the corpus striatum, dopamine encounters its receptors and produces multiple actions. Dopamine serves an inhibitory function, slowing the flow of impulses down spinal neurons. When dopamine is present, the normal flow of motor impulses from the corpus striatum helps to produce coordinated unconscious muscle movement.