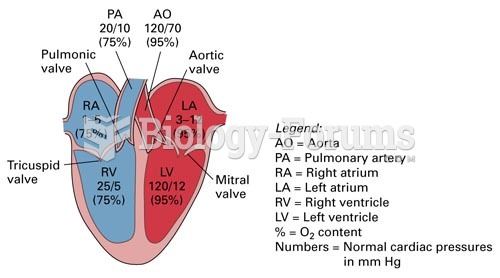
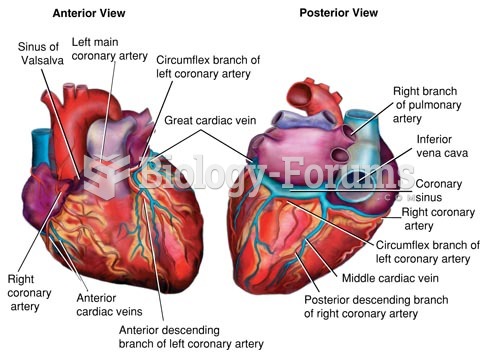
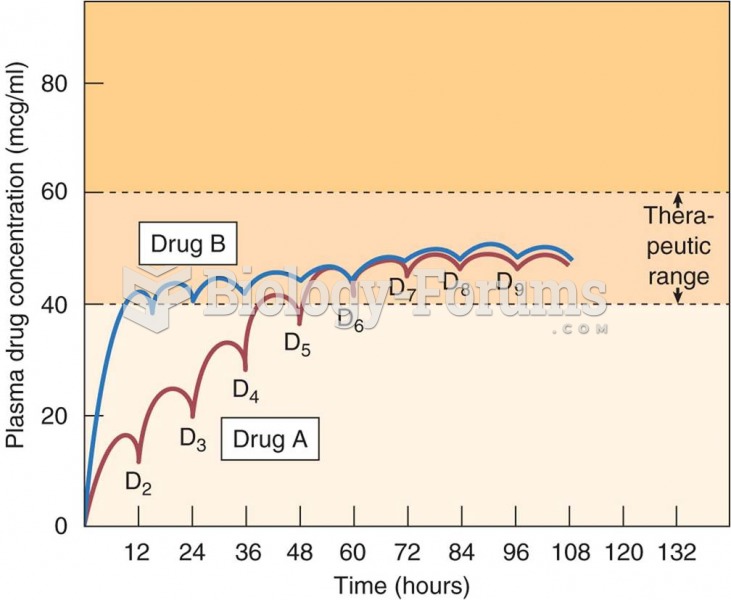
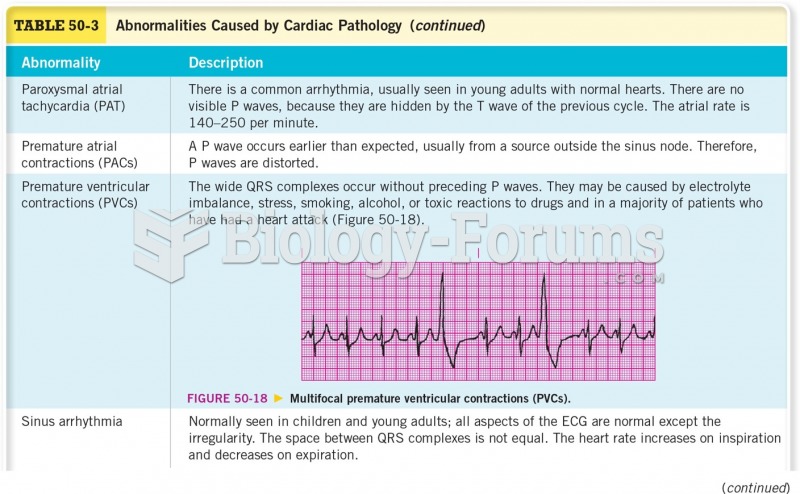
|
|
|
Walt Disney helped combat malaria by making an animated film in 1943 called The Winged Scourge. This short film starred the seven dwarfs and taught children that mosquitos transmit malaria, which is a very bad disease. It advocated the killing of mosquitos to stop the disease.
Oliver Wendell Holmes is credited with introducing the words "anesthesia" and "anesthetic" into the English language in 1846.
HIV testing reach is still limited. An estimated 40% of people with HIV (more than 14 million) remain undiagnosed and do not know their infection status.
The ratio of hydrogen atoms to oxygen in water (H2O) is 2:1.
There used to be a metric calendar, as well as metric clocks. The metric calendar, or "French Republican Calendar" divided the year into 12 months, but each month was divided into three 10-day weeks. Each day had 10 decimal hours. Each hour had 100 decimal minutes. Due to lack of popularity, the metric clocks and calendars were ended in 1795, three years after they had been first marketed.