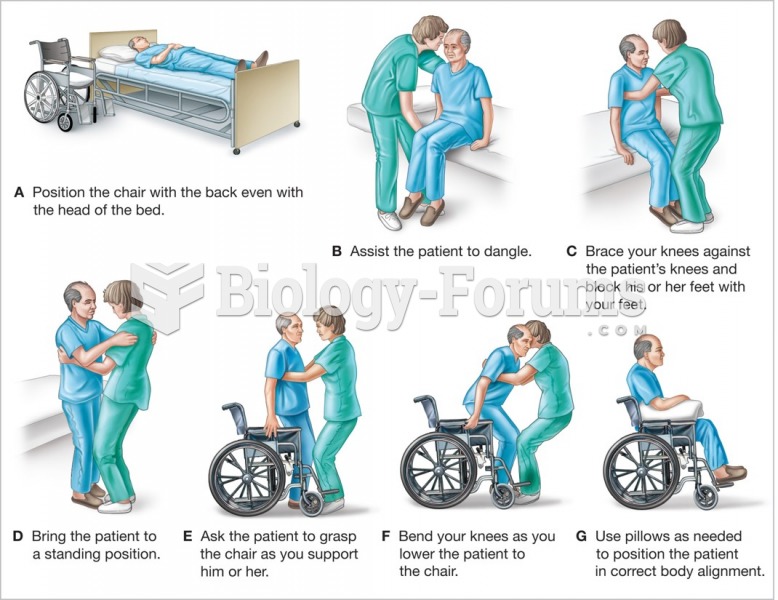
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
The term bacteria was devised in the 19th century by German biologist Ferdinand Cohn. He based it on the Greek word "bakterion" meaning a small rod or staff. Cohn is considered to be the father of modern bacteriology.
Did you know?
There are more bacteria in your mouth than there are people in the world.
Did you know?
Inotropic therapy does not have a role in the treatment of most heart failure patients. These drugs can make patients feel and function better but usually do not lengthen the predicted length of their lives.
Did you know?
The highest suicide rate in the United States is among people ages 65 years and older. Almost 15% of people in this age group commit suicide every year.
Did you know?
Thyroid conditions cause a higher risk of fibromyalgia and chronic fatigue syndrome.