|
|
|
Nearly all drugs pass into human breast milk. How often a drug is taken influences the amount of drug that will pass into the milk. Medications taken 30 to 60 minutes before breastfeeding are likely to be at peak blood levels when the baby is nursing.
Green tea is able to stop the scent of garlic or onion from causing bad breath.
Aspirin is the most widely used drug in the world. It has even been recognized as such by the Guinness Book of World Records.
Automated pill dispensing systems have alarms to alert patients when the correct dosing time has arrived. Most systems work with many varieties of medications, so patients who are taking a variety of drugs can still be in control of their dose regimen.
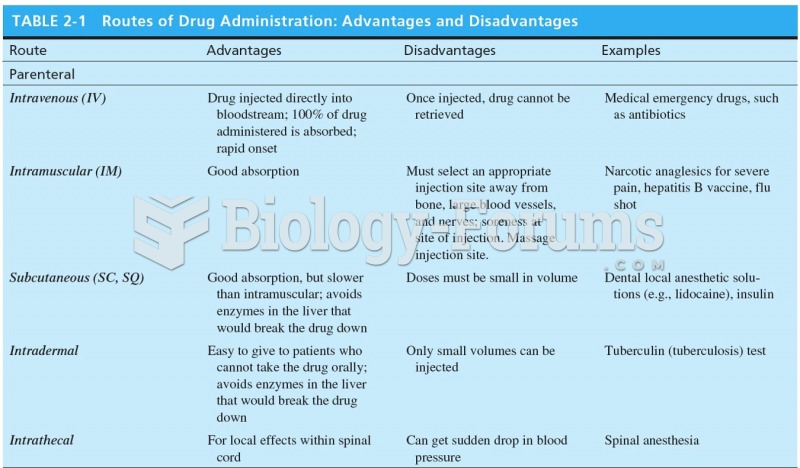
By definition, when a medication is administered intravenously, its bioavailability is 100%.