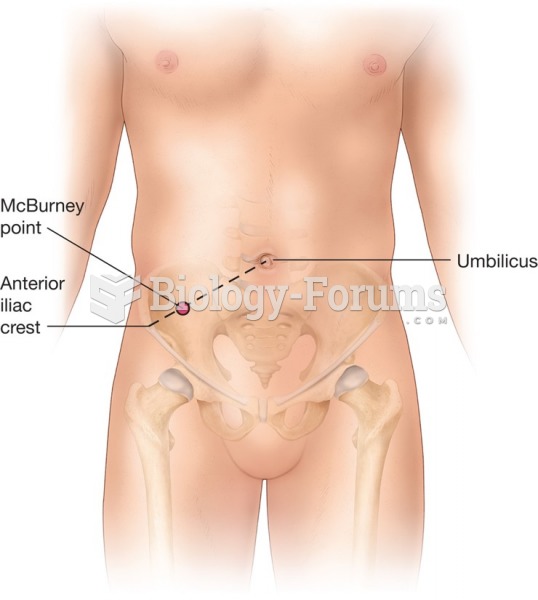
|
|
|
Signs and symptoms of a drug overdose include losing consciousness, fever or sweating, breathing problems, abnormal pulse, and changes in skin color.
Adult head lice are gray, about ? inch long, and often have a tiny dot on their backs. A female can lay between 50 and 150 eggs within the several weeks that she is alive. They feed on human blood.
Bacteria have flourished on the earth for over three billion years. They were the first life forms on the planet.
Certain chemicals, after ingestion, can be converted by the body into cyanide. Most of these chemicals have been removed from the market, but some old nail polish remover, solvents, and plastics manufacturing solutions can contain these substances.
As many as 28% of hospitalized patients requiring mechanical ventilators to help them breathe (for more than 48 hours) will develop ventilator-associated pneumonia. Current therapy involves intravenous antibiotics, but new antibiotics that can be inhaled (and more directly treat the infection) are being developed.