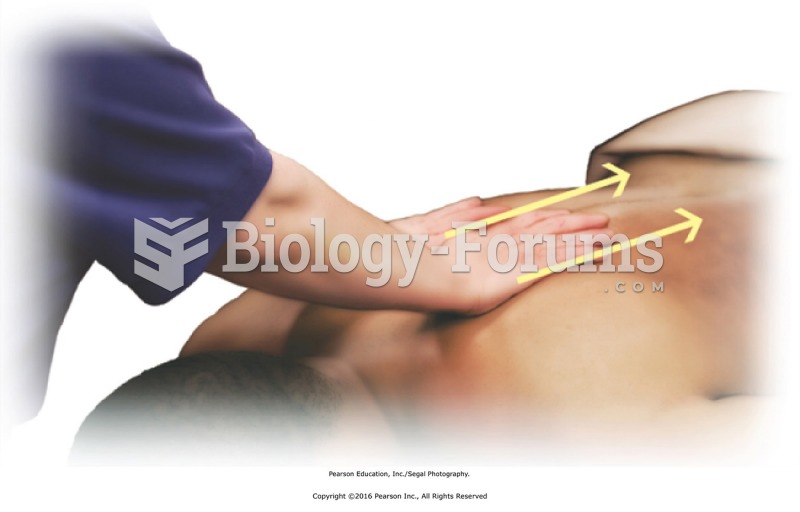
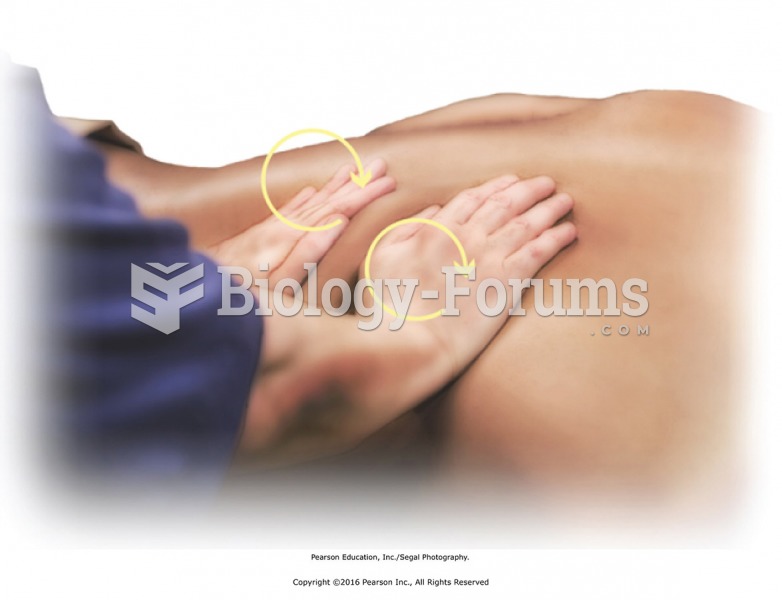
|
|
|
More than 4.4billion prescriptions were dispensed within the United States in 2016.
The FDA recognizes 118 routes of administration.
The U.S. Pharmacopeia Medication Errors Reporting Program states that approximately 50% of all medication errors involve insulin.
Interferon was scarce and expensive until 1980, when the interferon gene was inserted into bacteria using recombinant DNA technology, allowing for mass cultivation and purification from bacterial cultures.
Over time, chronic hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus infections can progress to advanced liver disease, liver failure, and hepatocellular carcinoma. Unlike other forms, more than 80% of hepatitis C infections become chronic and lead to liver disease. When combined with hepatitis B, hepatitis C now accounts for 75% percent of all cases of liver disease around the world. Liver failure caused by hepatitis C is now leading cause of liver transplants in the United States.
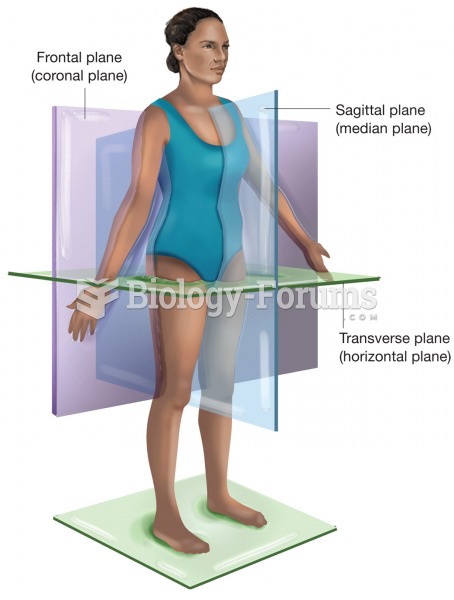 The planes of the body. The sagittal plane is vertical from front to back, the frontal plane is vert
The planes of the body. The sagittal plane is vertical from front to back, the frontal plane is vert
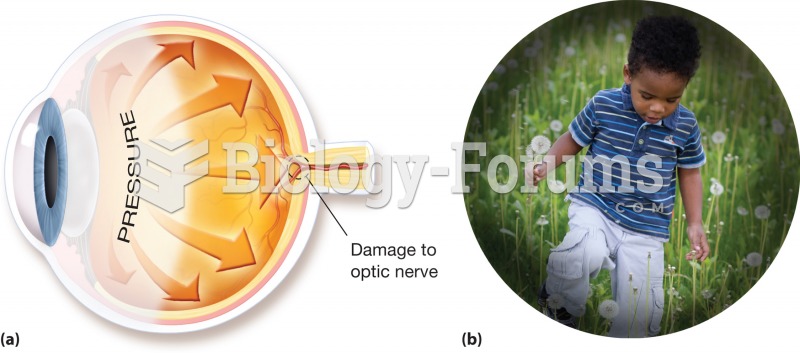 Glaucoma. (a) A buildup of pressure within the eye cavities, often caused by a blockage of vessels t
Glaucoma. (a) A buildup of pressure within the eye cavities, often caused by a blockage of vessels t
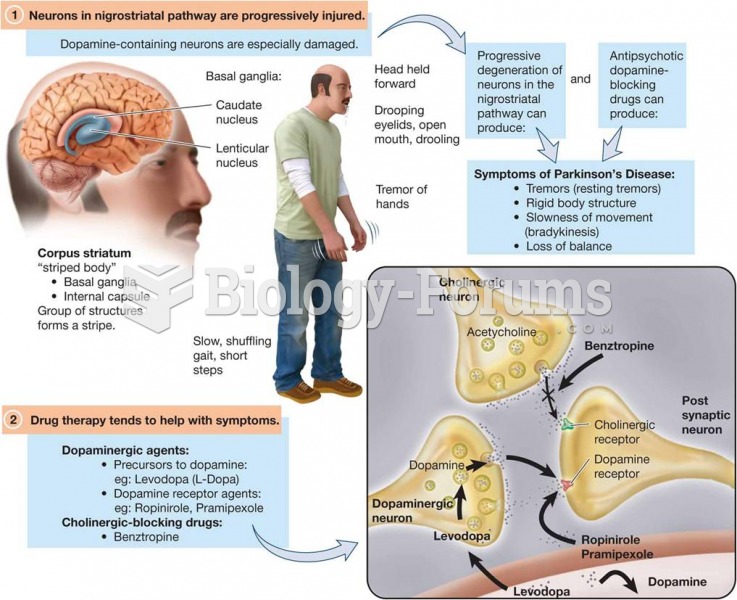 Antiparkinson Drugs Focus on Restoring Dopamine Function and Blocking Cholinergic Activity in the Ni
Antiparkinson Drugs Focus on Restoring Dopamine Function and Blocking Cholinergic Activity in the Ni