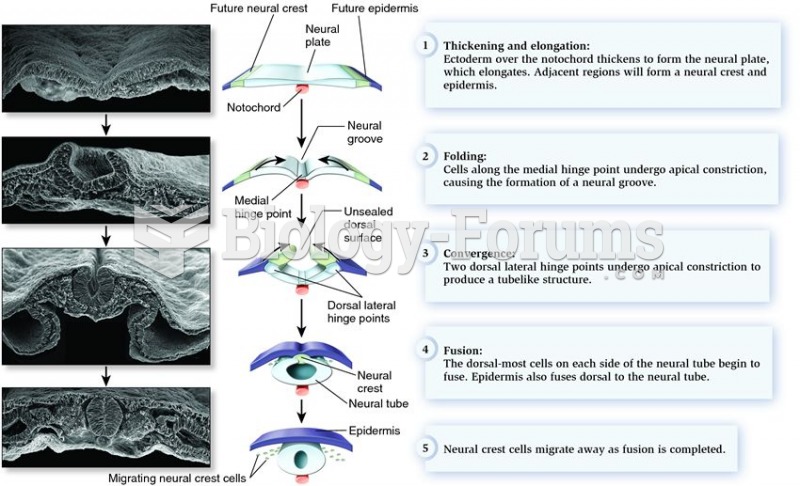
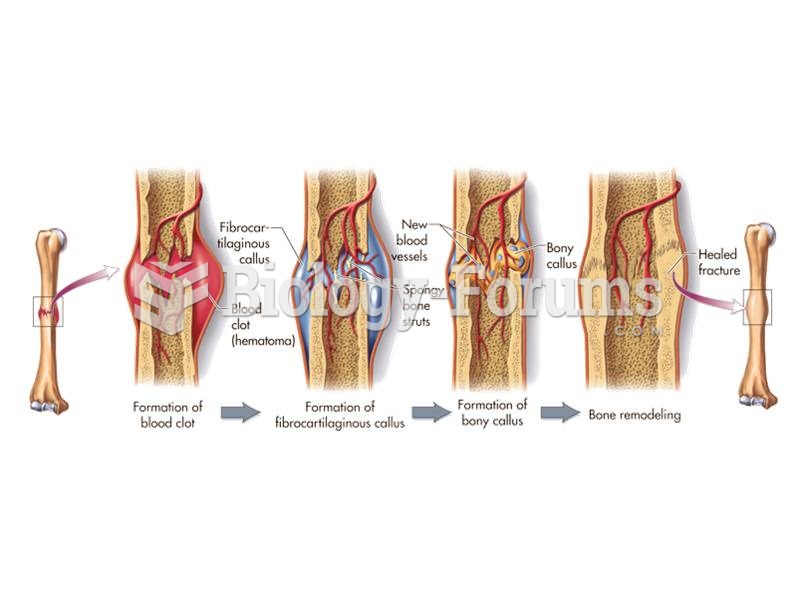
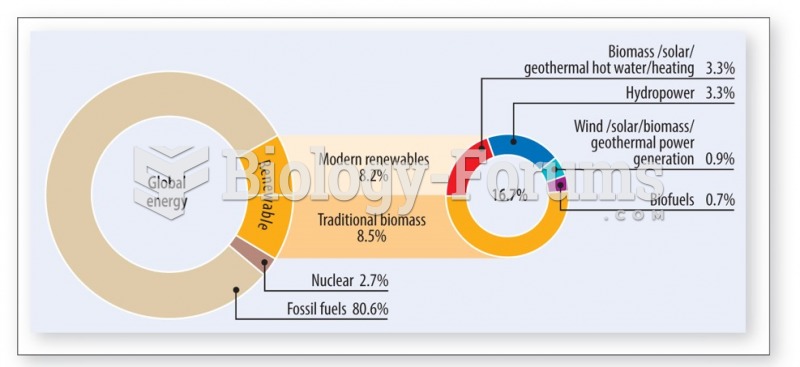
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Human kidneys will clean about 1 million gallons of blood in an average lifetime.
Did you know?
Your heart beats over 36 million times a year.
Did you know?
Critical care patients are twice as likely to receive the wrong medication. Of these errors, 20% are life-threatening, and 42% require additional life-sustaining treatments.
Did you know?
More than 150,000 Americans killed by cardiovascular disease are younger than the age of 65 years.
Did you know?
The types of cancer that alpha interferons are used to treat include hairy cell leukemia, melanoma, follicular non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, and AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma.