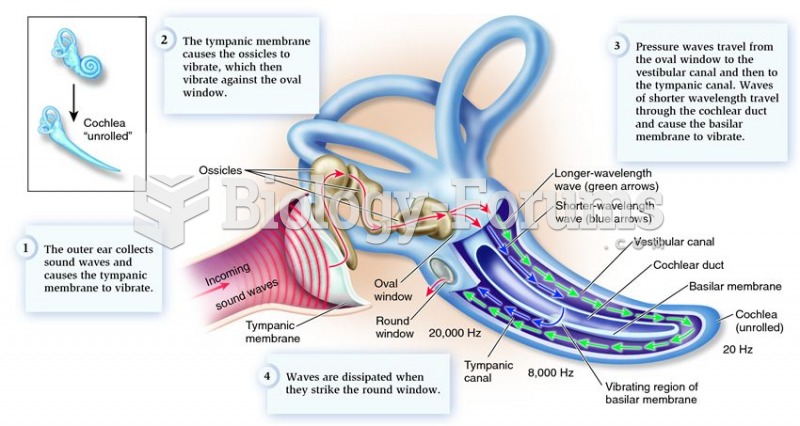
|
|
|
Interferon was scarce and expensive until 1980, when the interferon gene was inserted into bacteria using recombinant DNA technology, allowing for mass cultivation and purification from bacterial cultures.
There are more sensory neurons in the tongue than in any other part of the body.
The first successful kidney transplant was performed in 1954 and occurred in Boston. A kidney from an identical twin was transplanted into his dying brother's body and was not rejected because it did not appear foreign to his body.
When Gabriel Fahrenheit invented the first mercury thermometer, he called "zero degrees" the lowest temperature he was able to attain with a mixture of ice and salt. For the upper point of his scale, he used 96°, which he measured as normal human body temperature (we know it to be 98.6° today because of more accurate thermometers).
Drug abusers experience the following scenario: The pleasure given by their drug (or drugs) of choice is so strong that it is difficult to eradicate even after years of staying away from the substances involved. Certain triggers may cause a drug abuser to relapse. Research shows that long-term drug abuse results in significant changes in brain function that persist long after an individual stops using drugs. It is most important to realize that the same is true of not just illegal substances but alcohol and tobacco as well.