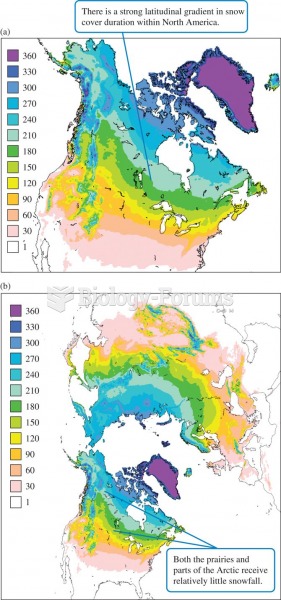
|
|
|
Nearly all drugs pass into human breast milk. How often a drug is taken influences the amount of drug that will pass into the milk. Medications taken 30 to 60 minutes before breastfeeding are likely to be at peak blood levels when the baby is nursing.
Common abbreviations that cause medication errors include U (unit), mg (milligram), QD (every day), SC (subcutaneous), TIW (three times per week), D/C (discharge or discontinue), HS (at bedtime or "hours of sleep"), cc (cubic centimeters), and AU (each ear).
Malaria mortality rates are falling. Increased malaria prevention and control measures have greatly improved these rates. Since 2000, malaria mortality rates have fallen globally by 60% among all age groups, and by 65% among children under age 5.
Patients who cannot swallow may receive nutrition via a parenteral route—usually, a catheter is inserted through the chest into a large vein going into the heart.
Approximately one in three babies in the United States is now delivered by cesarean section. The number of cesarean sections in the United States has risen 46% since 1996.